Targeted Delivery of Arctigenin Using Sialic Acid Conjugate-Modified Liposomes for the Treatment of Breast Cancer
- PMID: 38202860
- PMCID: PMC10781120
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules29010278
Targeted Delivery of Arctigenin Using Sialic Acid Conjugate-Modified Liposomes for the Treatment of Breast Cancer
Abstract
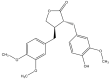
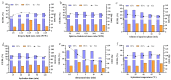
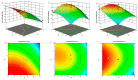
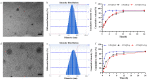
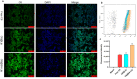
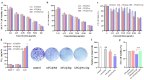
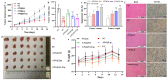
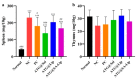
Arctigenin (ATG) is a broad-spectrum antitumor drug with an excellent inhibitory effect on malignant tumors such as breast cancer, glioblastoma, liver cancer, and colon cancer. However, the clinical application of ATG is limited by its poor water solubility and quick hydrolysis in the liver, intestine, and plasma, which might hinder its application. Sialic acid (SA) recognizes selectin receptors overexpressed on the surface of tumor-associated macrophages. In this study, SA was conjugated with octadecylamine (ODA) to prepare SA-ODA, which was employed to prepare SA functionalized nanoliposomes (SA-Lip) to achieve breast cancer targeting. The formulations were finely optimized using the Box-Behnken design to achieve higher ATG loading. The size, ζ potential, entrapment efficiency, drug loading, and release behavior of ATG@SA-Lip were fully investigated in comparison with conventional ATG@Lip. The ATG@SA-Lip displayed more potent cytotoxicity and higher cellular internalization compared to ATG@Sol and ATG@Lip in both MCF7 and 4T1 cells. Notably, ATG@SA-Lip showed the lowest impact on the immune system. Our study demonstrates that SA-Lip has strong potential as a delivery system for the targeted delivery of ATG.
Keywords: antitumor in vivo; arctigenin; nanoliposomes; sialic acid receptor; targeted delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Are third-generation active-targeting nanoformulations definitely the best? In vitro and in vivo comparisons of pixantrone-loaded liposomes modified with different sialic acid derivatives.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Mar;12(3):647-661. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-00973-y. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 33928513
-
The anticancer efficacy of pixantrone-loaded liposomes decorated with sialic acid-octadecylamine conjugate.Biomaterials. 2014 Jun;35(19):5216-25. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.03.022. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Biomaterials. 2014. PMID: 24703714
-
Sialic acid-decorated liposomes enhance the anti-cancer efficacy of docetaxel in tumor-associated macrophages.Biomater Adv. 2023 Nov;154:213606. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2023.213606. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Biomater Adv. 2023. PMID: 37678087
-
Hyaluronic acid-modified liposomal honokiol nanocarrier: Enhance anti-metastasis and antitumor efficacy against breast cancer.Carbohydr Polym. 2020 May 1;235:115981. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115981. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Carbohydr Polym. 2020. PMID: 32122511 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of the action of Arctigenin in cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Dec;108:403-407. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.158. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30236849 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic and Therapeutic Implications of Protein and Lipid Sialylation in Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 7;25(22):11962. doi: 10.3390/ijms252211962. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant metabolites and functional foods in metastatic breast cancer: a supportive strategy for management.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jul 23;16:1631232. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1631232. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40771913 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shabgah A.G., Suksatan W., Achmad M.H., Bokov D.O., Abdelbasset W.K., Ezzatifar F., Hemmati S., Mohammadi H., Soleimani D., Jadidi-Niaragh F., et al. Arctigenin, an antitumor agent; a cutting-edge topic and up-to-the-minute approach in cancer treatment. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021;909:174419. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174419. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

