A Hybrid Protection Scheme for the Gait Analysis in Early Dementia Recognition
- PMID: 38202886
- PMCID: PMC10780691
- DOI: 10.3390/s24010024
A Hybrid Protection Scheme for the Gait Analysis in Early Dementia Recognition
Abstract
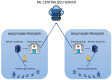
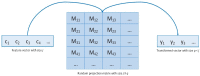
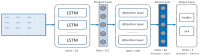
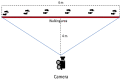
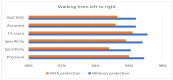
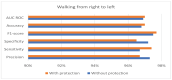
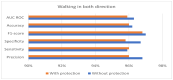
Human activity recognition (HAR) through gait analysis is a very promising research area for early detection of neurodegenerative diseases because gait abnormalities are typical symptoms of some neurodegenerative diseases, such as early dementia. While working with such biometric data, the performance parameters must be considered along with privacy and security issues. In other words, such biometric data should be processed under specific security and privacy requirements. This work proposes an innovative hybrid protection scheme combining a partially homomorphic encryption scheme and a cancelable biometric technique based on random projection to protect gait features, ensuring patient privacy according to ISO/IEC 24745. The proposed hybrid protection scheme has been implemented along a long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network to realize a secure early dementia diagnosis system. The proposed protection scheme is scalable and implementable with any type of neural network because it is independent of the network's architecture. The conducted experiments demonstrate that the proposed protection scheme enables a high trade-off between safety and performance. The accuracy degradation is at most 1.20% compared with the early dementia recognition system without the protection scheme. Moreover, security and computational analyses of the proposed scheme have been conducted and reported.
Keywords: cancelable biometric; gait analysis; homomorphic cryptography; neurodegenerative disease; random projection; security healthcare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficient face information encryption and verification scheme based on full homomorphic encryption.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 3;15(1):11388. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95383-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40181009 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid approach to protect palmprint templates.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:686754. doi: 10.1155/2014/686754. Epub 2014 Mar 27. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24982977 Free PMC article.
-
A cancelable biometric scheme based on multi-lead ECGs.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2017 Jul;2017:3497-3500. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2017.8037610. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2017. PMID: 29060651
-
Double random phase encoding for cancelable face and iris recognition.Appl Opt. 2018 Dec 10;57(35):10305-10316. doi: 10.1364/AO.57.010305. Appl Opt. 2018. PMID: 30645240
-
Real-Time Remote Health Monitoring Systems Using Body Sensor Information and Finger Vein Biometric Verification: A Multi-Layer Systematic Review.J Med Syst. 2018 Oct 16;42(12):238. doi: 10.1007/s10916-018-1104-5. J Med Syst. 2018. PMID: 30327939
Cited by
-
Securing gait recognition with homomorphic encryption.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 12;15(1):29528. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14047-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40796590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dentamaro V., Impedovo D., Pirlo G. Gait Analysis for Early Neurodegenerative Diseases Classification Through the Kinematic Theory of Rapid Human Movements. IEEE Access. 2020;8:193966–193980. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3032202. - DOI
-
- Cao Z., Simon T., Wei S.-E., Sheikh Y. Realtime Multi-person 2D Pose Estimation Using Part Affinity Fields; Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); Honolulu, HI, USA. 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1302–1310.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

