Electrochemical Properties of PEDOT:PSS/Graphene Conductive Layers in Artificial Sweat
- PMID: 38202900
- PMCID: PMC10780959
- DOI: 10.3390/s24010039
Electrochemical Properties of PEDOT:PSS/Graphene Conductive Layers in Artificial Sweat
Abstract
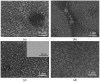
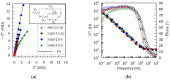
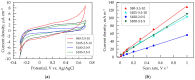
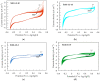
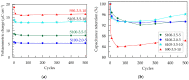
Electrodes based on PEDOT:PSS are gaining increasing importance as conductive electrodes and functional layers in various sensors and biosensors due to their easy processing and biocompatibility. This study investigates PEDOT:PSS/graphene layers deposited via spray coating on flexible PET substrates. The layers are characterized in terms of their morphology, roughness (via AFM and SEM), and electrochemical properties in artificial sweat using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and cyclic voltammetry (CV). The layers exhibit dominant capacitive behavior at low frequencies, with cut-off frequencies determined for thicker layers at 1 kHz. The equivalent circuit used to fit the EIS data reveals a resistance of about three orders of magnitude higher inside the layer compared to the charge transfer resistance at the solid/liquid interface. The capacitance values determined from the CV curves range from 54.3 to 122.0 mF m-2. After 500 CV cycles in a potential window of 1 V (from -0.3 to 0.7 V), capacitance retention for most layers is around 94%, with minimal surface changes being observed in the layers. The results suggest practical applications for PEDOT:PSS/graphene layers, both for high-frequency impedance measurements related to the functioning of individual organs and systems, such as impedance electrocardiography, impedance plethysmography, and respiratory monitoring, and as capacitive electrodes in the low-frequency range, realized as layered PEDOT:PSS/graphene conductive structures for biosignal recording.
Keywords: artificial sweat; conductive polymer; cyclic voltammetry; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; spray coating.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Electrochemical Investigation of PEDOT:PSS/Graphene Aging in Artificial Sweat.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jun 14;16(12):1706. doi: 10.3390/polym16121706. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38932055 Free PMC article.
-
Pedot:PSS/Graphene Oxide (GO) Ternary Nanocomposites for Electrochemical Applications.Molecules. 2023 Mar 26;28(7):2963. doi: 10.3390/molecules28072963. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37049728 Free PMC article.
-
Combining PEDOT:PSS Polymer Coating with Metallic 3D Nanowires Electrodes to Achieve High Electrochemical Performances for Neuronal Interfacing Applications.Adv Mater. 2023 Sep;35(39):e2302472. doi: 10.1002/adma.202302472. Epub 2023 Jul 23. Adv Mater. 2023. PMID: 37385261
-
Review on PEDOT:PSS-Based Conductive Fabric.ACS Omega. 2022 Sep 30;7(40):35371-35386. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c01834. eCollection 2022 Oct 11. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36249401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods of poly(3,4)-ethylenedioxithiophene (PEDOT) electrodeposition on metal electrodes for neural stimulation and recording.J Neural Eng. 2023 Jan 31;20(1). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/acb084. J Neural Eng. 2023. PMID: 36603213 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrochemical Investigation of PEDOT:PSS/Graphene Aging in Artificial Sweat.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jun 14;16(12):1706. doi: 10.3390/polym16121706. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38932055 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Surface Texture in Additively Manufactured Biocompatible Materials and Triboelectric Behavior.Materials (Basel). 2025 Jul 17;18(14):3366. doi: 10.3390/ma18143366. Materials (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40731576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Nanorod Arrays-Based Organic Electrochemical Transistor for SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Detection in Artificial Saliva.ACS Sens. 2025 Mar 28;10(3):2007-2018. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.4c03207. Epub 2025 Mar 13. ACS Sens. 2025. PMID: 40080450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dauzon E., Mansour A.E., Niazi M.R., Munir R., Smilgies D.-M., Sallenave X., Plesse C., Goubard F., Amassian A. Conducting and Stretchable PEDOT:PSS Electrodes: Role of Additives on Self-Assembly, Morphology, and Transport. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2019;11:17570–17582. doi: 10.1021/acsami.9b00934. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kouhnavard M., Yifan D., D’ Arcy J.M., Mishra R., Biswas P. Highly Conductive PEDOT Films with Enhanced Catalytic Activity for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Sol. Energy. 2020;211:258–264. doi: 10.1016/j.solener.2020.09.059. - DOI
-
- Kaur G., Kaur A., Kaur H. Review on Nanomaterials/Conducting Polymer-Based Nanocomposites for the Development of Biosensors and Electrochemical Sensors. Polym. Plast. Technol. Mater. 2020;60:502–519. doi: 10.1080/25740881.2020.1844233. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

