Impact of Starting Knee Flexion Angle on Muscle Activity and Performance during Plyometrics without Jumping
- PMID: 38202906
- PMCID: PMC10780924
- DOI: 10.3390/s24010044
Impact of Starting Knee Flexion Angle on Muscle Activity and Performance during Plyometrics without Jumping
Abstract
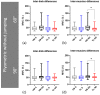
Most of the existing research has focused on jump plyometrics, where landing reaction forces must be dissipated among lower limb articulations. In contrast, the investigation of resisted plyometrics without jumping, devoid of such landing forces, remains relatively limited. This study aimed to (i) investigate the impact of resisted plyometrics without jumping at two knee flexion angles (60 and 90 degrees) on vastus muscle activity relative to limb dominance and (ii) assess strength, power, and work during the concentric-eccentric phases of these exercises. Thirty-one healthy participants underwent quantification of lower limb muscle amplitude, strength, power, and work during resisted plyometrics without jumping from both 60° and 90° knee flexion positions. After anthropometric evaluations, participants used a dynamometer with a load equal to 80% of body weight while wireless surface electromyography electrodes recorded data. Statistical analyses utilized paired t-tests or nonparametric equivalents and set significance at p ≤ 0.05. Results showed significantly higher muscle activity in the vastus medialis (VM) (dominant: 47.4%, p = 0.0008, rs = 0.90; nondominant: 54.8%, p = 0.047, rs = 0.88) and vastus lateralis (VL) (dominant: 46.9%, p = 0.0004, rs = 0.86; nondominant: 48.1%, p = 0.021, rs = 0.67) muscles when exercises started at 90° knee flexion, regardless of limb dominance. Substantial intermuscle differences occurred at both 60° (50.4%, p = 0.003, rs = 0.56) and 90° (54.8%, p = 0.005, rs = 0.62) knee flexion, favoring VM in the nondominant leg. Concentric and eccentric strength, power, and work metrics significantly increased when initiating exercises from a 90° position. In conclusion, commencing resisted plyometrics without jumping at a 90° knee flexion position increases VM and VL muscle activity, regardless of limb dominance. Furthermore, it enhances strength, power, and work, emphasizing the importance of knee flexion position customization for optimizing muscle engagement and functional performance.
Keywords: dynamometry; electromyography; limb dominance; physical training muscle strength; plyometric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Behm D.G., Young J.D., Whitten J.H.D., Reid J.C., Quigley P.J., Low J., Li Y., Lima C.D., Hodgson D.D., Chaouachi A., et al. Effectiveness of Traditional Strength vs. Power Training on Muscle Strength, Power and Speed with Youth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2017;8:423. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00423. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ramirez-Campillo R., Moran J., Chaabene H., Granacher U., Behm D.G., García-Hermoso A., Izquierdo M. Methodological characteristics and future directions for plyometric jump training research: A scoping review update. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports. 2020;30:983–997. doi: 10.1111/sms.13633. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

