Leptin-Mediated Induction of IL-6 Expression in Hofbauer Cells Contributes to Preeclampsia Pathogenesis
- PMID: 38203306
- PMCID: PMC10778808
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010135
Leptin-Mediated Induction of IL-6 Expression in Hofbauer Cells Contributes to Preeclampsia Pathogenesis
Abstract
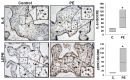
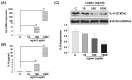
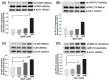
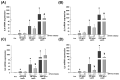
Leptin plays a crucial role in regulating energy homoeostasis, neuroendocrine function, metabolism, and immune and inflammatory responses. The adipose tissue is a main source of leptin, but during pregnancy, leptin is also secreted primarily by the placenta. Circulating leptin levels peak during the second trimester of human pregnancy and fall after labor. Several studies indicated a strong association between elevated placental leptin levels and preeclampsia (PE) pathogenesis and elevated serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels in PE patients. Therefore, we hypothesized that a local increase in placental leptin production induces IL-6 production in Hofbauer cells (HBCs) to contribute to PE-associated inflammation. We first investigated HBCs-specific IL-6 and leptin receptor (LEPR) expression and compared their immunoreactivity in PE vs. gestational age-matched control placentas. Subsequently, we examined the in vitro regulation of IL-6 as well as the phosphorylation levels of intracellular signaling proteins STAT3, STAT5, NF-κB, and ERK1/2 by increasing recombinant human leptin concentrations (10 to 1000 ng/mL) in primary cultured HBCs. Lastly, HBC cultures were incubated with leptin ± specific inhibitors of STAT3 or STAT5, or p65 NF-κB or ERK1/2 MAPK signaling cascades to determine relevant cascade(s) involved in leptin-mediated IL-6 regulation. Immunohistochemistry revealed ~three- and ~five-fold increases in IL-6 and LEPR expression, respectively, in HBCs from PE placentas. In vitro analysis indicated that leptin treatment in HBCs stimulate IL-6 in a concentration-dependent manner both at the transcriptional and secretory levels (p < 0.05). Moreover, leptin-treated HBC cultures displayed significantly increased phosphorylation levels of STAT5, p65 NF-κB, and ERK1/2 MAPK and pre-incubation of HBCs with a specific ERK1/2 MAPK inhibitor blocked leptin-induced IL-6 expression. Our in situ results show that HBCs contribute to the pathogenesis of PE by elevating IL-6 expression, and in vitro results indicate that induction of IL-6 expression in HBCs is primarily leptin-mediated. While HBCs display an anti-inflammatory phenotype in normal placentas, elevated levels of leptin may transform HBCs into a pro-inflammatory phenotype by activating ERK1/2 MAPK to augment IL-6 expression.
Keywords: ERK1/2; Hofbauer cells; IL-6; JAK/STAT; NF-κB; leptin; placenta; preeclampsia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Placental macrophages present distinct polarization pattern and effector functions depending on clinical onset of preeclampsia.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 12;13:1095879. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1095879. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36713449 Free PMC article.
-
Placental Macrophage (Hofbauer Cell) Responses to Infection During Pregnancy: A Systematic Scoping Review.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 11;12:756035. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.756035. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35250964 Free PMC article.
-
Hofbauer Cells Spread Listeria monocytogenes among Placental Cells and Undergo Pro-Inflammatory Reprogramming while Retaining Production of Tolerogenic Factors.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0184921. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01849-21. Epub 2021 Aug 17. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34399615 Free PMC article.
-
Human Placental Hofbauer Cells Maintain an Anti-inflammatory M2 Phenotype despite the Presence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Front Immunol. 2017 Jul 31;8:888. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00888. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28824621 Free PMC article.
-
NFĸB and its inhibitors in preeclampsia: mechanisms and potential interventions.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 29. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04211-x. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40299024 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-Cell Transcriptome and RNA Sequencing Reveal Immune-Related Markers of Preeclampsia.Reprod Sci. 2025 Aug;32(8):2819-2828. doi: 10.1007/s43032-025-01843-5. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Reprod Sci. 2025. PMID: 40216654 Free PMC article.
-
Causal association of obesity and chronic pain mediated by educational attainment and smoking: a mediation Mendelian randomization study.Korean J Pain. 2025 Apr 1;38(2):177-186. doi: 10.3344/kjp.24331. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Korean J Pain. 2025. PMID: 40044590 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct TYRO3 and PROS1 expression levels contribute to preeclampsia pathogenesis.Histochem Cell Biol. 2025 Jan 29;163(1):29. doi: 10.1007/s00418-024-02351-4. Histochem Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 39878883
References
-
- Barrichon M., Hadi T., Wendremaire M., Ptasinski C., Seigneuric R., Marcion G., Delignette M., Marchet J., Dumas M., Sagot P., et al. Dose-dependent biphasic leptin-induced proliferation is caused by non-specific IL-6/NF-kappaB pathway activation in human myometrial cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015;172:2974–2990. doi: 10.1111/bph.13100. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lappas M., Permezel M., Rice G.E. Leptin and adiponectin stimulate the release of proinflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins from human placenta and maternal adipose tissue via nuclear factor-kappaB, peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptor-gamma and extracellularly regulated kinase 1/2. Endocrinology. 2005;146:3334–3342. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

