Enhancement of Immune Functions by Limosilactobacillus reuteri KBL346: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
- PMID: 38203313
- PMCID: PMC10779160
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010141
Enhancement of Immune Functions by Limosilactobacillus reuteri KBL346: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Abstract
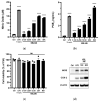
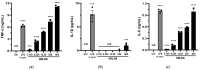
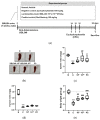
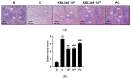
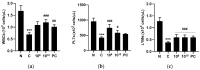
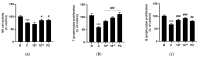
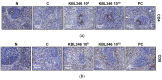
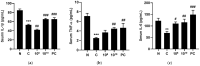
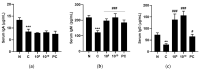
Lactobacilli have been widely used as probiotics because of their benefits for intestinal health and physiological functions. Among a variety of Lactobacillus genera, Limosilactobacillus reuteri has been studied for its ability to exert anti-inflammatory functions and its role in controlling metabolic disorders, as well as the production of the antimicrobial compound reuterin. However, the effects and mechanisms of L. reuteri on enhancing immune responses in the immunosuppressed states have been relatively understudied. In this study, we isolated an immunomodulatory strain, namely, L. reuteri KBL346 (KBL346), from a fecal sample of a 3-month-old infant in Korea. We evaluated the immunostimulatory activity and hematopoietic function of KBL346 in macrophages and cyclophosphamide (CPA)-induced immunosuppressed mice. KBL346 increased the phagocytic activity against Candida albicans MYA-4788 in macrophages, and as biomarkers for this, increased secretions of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) were confirmed. Also, the secretions of innate cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) were increased. In CPA-induced immunosuppressed mice, KBL346 at a dosage of 1010 CFU/kg protected against spleen injury and suppressed levels of immune-associated parameters, including NK cell activity, T and B lymphocyte proliferation, CD4+ and CD8+ T cell abundance, cytokines, and immunoglobulins in vivo. The effects were comparable or superior to those in the Korean red ginseng positive control group. Furthermore, the safety assessment of KBL346 as a probiotic was conducted by evaluating its antibiotic resistance, hemolytic activity, cytotoxicity, and metabolic characteristics. This study demonstrated the efficacy and safety of KBL346, which could potentially be used as a supplement to enhance the immune system.
Keywords: Limosilactobacillus reuteri; cyclophosphamide; immunity; macrophage; probiotics; safety.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Oral Administration of Limosilactobacillus reuteri KBL346 Ameliorates Influenza Virus A/PR8 Infection in Mouse.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Jun 29. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10301-8. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 38949757
-
Modulating effects of heat-killed and live Limosilactobacillus reuteri PSC102 on the immune response and gut microbiota of cyclophosphamide-treated rats.Vet Q. 2024 Dec;44(1):1-18. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2024.2344765. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Vet Q. 2024. PMID: 38682319 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota and Probiotics: The Role of Limosilactobacillus Reuteri in Diverticulitis.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Aug 5;57(8):802. doi: 10.3390/medicina57080802. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34441008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri on Cell Viability and PGE2 Production in Human Gingival Fibroblasts.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2017 Sep;9(3):278-283. doi: 10.1007/s12602-016-9246-6. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2017. PMID: 28028690
-
Limosilactobacillus reuteri - a probiotic gut commensal with contextual impact on immunity.Gut Microbes. 2025 Dec;17(1):2451088. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2025.2451088. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Gut Microbes. 2025. PMID: 39825615 Review.
Cited by
-
Recombinant Bacillus subtilis Displaying DHAV-1 VP1 Protein as a Dual-Function Probiotic: Evaluation of Immunological Efficacy, Growth Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, and Intestinal Health in Cherry Valley Ducks.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Aug 15. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10720-1. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40815365
-
Probiotic Limosilactobacillus reuteri KUB-AC5 decreases urothelial cell invasion and enhances macrophage killing of uropathogenic Escherichia coli in vitro study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 18;14:1401462. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1401462. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39091675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han S.K., Shin Y.J., Lee D.Y., Kim K.M., Yang S.J., Kim D.S., Choi J.W., Lee S., Kim D.H. Lactobacillus rhamnosus HDB1258 modulates gut microbiota-mediated immune response in mice with or without lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation. BMC Microbiol. 2021;21:146. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02192-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

