Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices: A Potential Platform to Study Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
- PMID: 38203321
- PMCID: PMC10778645
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010150
Human Precision-Cut Liver Slices: A Potential Platform to Study Alcohol-Related Liver Disease
Abstract
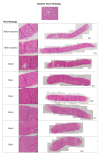
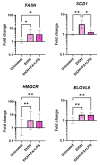
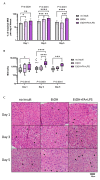
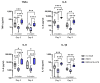
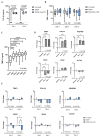
Alcohol-related liver disease (ALD) encompasses a range of pathological conditions that are complex to study at the clinical and preclinical levels. Despite the global burden of ALD, there is a lack of effective treatments, and mortality is high. One of the reasons for the unsuccessful development of novel therapies is that experimental studies are hindered by the challenge of recapitulating this multifactorial disorder in vitro, including the contributions of hepatotoxicity, impaired lipid metabolism, fibrosis and inflammatory cytokine storm, which are critical drivers in the pathogenesis of ALD in patients and primary targets for drug development. Here, we present the unique characteristics of the culture of human precision-cut liver slices (PCLS) to replicate key disease processes in ALD. PCLS were prepared from human liver specimens and treated with ethanol alone or in combination with fatty acids and lipopolysaccharide (FA + LPS) for up to 5 days to induce hepatotoxic, inflammatory and fibrotic events associated with ALD. Alcohol insult induced hepatocyte death which was more pronounced with the addition of FA + LPS. This mixture showed a significant increase in the cytokines conventionally associated with the prototypical inflammatory response observed in severe ALD, and interestingly, alcohol alone exhibited a different effect. Profibrogenic activation was also observed in the slices and investigated in the context of slice preparation. These results support the versatility of this organotypic model to study different pathways involved in alcohol-induced liver damage and ALD progression and highlight the applicability of the PCLS for drug discovery, confirming their relevance as a bridge between preclinical and clinical studies.
Keywords: alcoholic hepatitis; ethanol hepatotoxicity; ex vivo models; fibrosis; organotypic culture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Global Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2018. [(accessed on 13 December 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565639.
-
- Ndugga N., Lightbourne T.G., Javaherian K., Cabezas J., Verma N., Barritt A.S., Bataller R. Disparities between Research Attention and Burden in Liver Diseases: Implications on Uneven Advances in Pharmacological Therapies in Europe and the USA. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e013620. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013620. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lackner C., Stauber R.E., Davies S., Denk H., Dienes H.P., Gnemmi V., Guido M., Miquel R., Paradis V., Schirmacher P., et al. Development and Prognostic Relevance of a Histologic Grading and Staging System for Alcohol-Related Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2021;75:810–819. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.05.029. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

