Nickel Challenge In Vitro Affects CD38 and HLA-DR Expression in T Cell Subpopulations from the Blood of Patients with Nickel Allergy
- PMID: 38203472
- PMCID: PMC10778727
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010298
Nickel Challenge In Vitro Affects CD38 and HLA-DR Expression in T Cell Subpopulations from the Blood of Patients with Nickel Allergy
Abstract
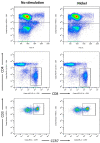
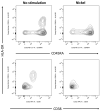
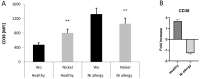
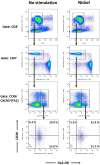
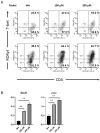
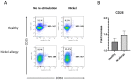
Nickel allergy is a major health problem and shows clinical manifestation of contact eczema. The response of specific lymphocyte subpopulations in sensitized patients after new challenge to nickel has until now not been studied in detail. To evaluate if nickel-based elicitation reaction could be objectively identified by multi-parametric flow cytometry, immunophenotyping of specific T cells was applied. White blood cells from 7 patients (4 positive in patch test, 3 negative) were challenged by nickel and in vitro short-term culture. Standardized antibody-dye combinations, specific for T helper(h)1, Th17 and cytotoxic T cell activation, were selected according to the recommendations of Stanford Human Immune Monitoring Center. In cytotoxic CD8+CCR7+CD45RA+ T cells from patients suffering from nickel allergy, CD38 and HLA-DR were elevated comparing to healthy donors. After challenge to nickel in vitro both markers decreased in CD8+CCR7+CD45RA+ T cells but found up-regulated in CD4+CCR7+CD45RA+CCR6-CXCR3+Th1 cells. Intracellular expression of T-bet and RORγt further indicated Th1 and Th17 cells. Finally, CD4+CD25+CCR4- T cells increased after challenge with nickel in PBMCs of patients with nickel allergy. Flow cytometry based quantification of T cell markers might be used as a specific and reliable method to detect chemical induced skin sensitization and confirm diagnostic patch testing in the clinics.
Keywords: T helper cells; cytotoxic T cells; flow cytometry; lymphocytes; nickel allergy; phenotyping.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Negative Clinical Evolution in COVID-19 Patients Is Frequently Accompanied With an Increased Proportion of Undifferentiated Th Cells and a Strong Underrepresentation of the Th1 Subset.Front Immunol. 2020 Nov 26;11:596553. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.596553. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33324414 Free PMC article.
-
Nickel-responding T cells are CD4+ CLA+ CD45RO+ and express chemokine receptors CXCR3, CCR4 and CCR10.Br J Dermatol. 2004 Jul;151(1):32-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2004.05975.x. Br J Dermatol. 2004. PMID: 15270870
-
Reference values for peripheral blood lymphocyte phenotypes applicable to the healthy adult population in Switzerland.Eur J Haematol. 2004 Mar;72(3):203-12. doi: 10.1046/j.0902-4441.2003.00199.x. Eur J Haematol. 2004. PMID: 14962239
-
Vitamin D modulates the expression of HLA-DR and CD38 after in vitro activation of T-cells.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017 Mar 1;29(3):93-103. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2016-0037. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017. PMID: 28222027
-
Mononuclear cell subsets in the nickel-allergic reaction in vitro and in vivo.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Apr;89(4):794-800. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90433-3. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1532806
References
-
- Peiser M., Tralau T., Heidler J., Api A.M., Arts J.H., Basketter D.A., English J., Diepgen T.L., Fuhlbrigge R.C., Gaspari A.A., et al. Allergic contact dermatitis: Epidemiology, molecular mechanisms, in vitro methods and regulatory aspects. Current knowledge assembled at an international workshop at BfR, Germany. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012;69:763–781. doi: 10.1007/s00018-011-0846-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

