Consideration of SHP-1 as a Molecular Target for Tumor Therapy
- PMID: 38203502
- PMCID: PMC10779157
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010331
Consideration of SHP-1 as a Molecular Target for Tumor Therapy
Abstract
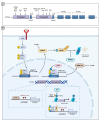
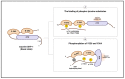
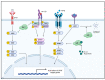
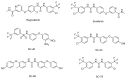
Abnormal activation of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) contributes to tumorigenesis, while protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) contribute to tumor control. One of the most representative PTPs is Src homology region 2 (SH2) domain-containing phosphatase 1 (SHP-1), which is associated with either an increased or decreased survival rate depending on the cancer type. Hypermethylation in the promoter region of PTPN6, the gene for the SHP-1 protein, is a representative epigenetic regulation mechanism that suppresses the expression of SHP-1 in tumor cells. SHP-1 comprises two SH2 domains (N-SH2 and C-SH2) and a catalytic PTP domain. Intramolecular interactions between the N-SH2 and PTP domains inhibit SHP-1 activity. Opening of the PTP domain by a conformational change in SHP-1 increases enzymatic activity and contributes to a tumor control phenotype by inhibiting the activation of the Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT3) pathway. Although various compounds that increase SHP-1 activation or expression have been proposed as tumor therapeutics, except sorafenib and its derivatives, few candidates have demonstrated clinical significance. In some cancers, SHP-1 expression and activation contribute to a tumorigenic phenotype by inducing a tumor-friendly microenvironment. Therefore, developing anticancer drugs targeting SHP-1 must consider the effect of SHP-1 on both cell biological mechanisms of SHP-1 in tumor cells and the tumor microenvironment according to the target cancer type. Furthermore, the use of combination therapies should be considered.
Keywords: Src homology region 2 (SH2) domain-containing phosphatase 1; anticancer drug; protein tyrosine phosphatases; receptor tyrosine kinases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Src homology region 2 (SH2) domain-containing phosphatase-1 dephosphorylates B cell linker protein/SH2 domain leukocyte protein of 65 kDa and selectively regulates c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase activation in B cells.J Immunol. 2000 Aug 1;165(3):1344-51. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.3.1344. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10903736
-
Dual signaling role of the protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 in regulating expression of acute-phase plasma proteins by interleukin-6 cytokine receptors in hepatic cells.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Aug;19(8):5326-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.8.5326. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10409724 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase 1 agonists from sorafenib for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2014 Jan;59(1):190-201. doi: 10.1002/hep.26640. Epub 2013 Dec 9. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 23908138
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2: a proto-oncogene product that promotes Ras activation.Cancer Sci. 2009 Oct;100(10):1786-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01257.x. Epub 2009 Jun 23. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19622105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategy for Leukemia Treatment Targeting SHP-1,2 and SHIP.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 19;9:730400. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.730400. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34490276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SHP1 and its downstream p38/SP1/PI3K/YAP/Notch-1 signaling in trophoblast cells suppressed the progression of Preeclampsia via inhibiting proliferation of SMCs.Sci Rep. 2025 May 9;15(1):16205. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00164-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40346122 Free PMC article.
-
The novel role of LOC344887 in the enhancement of hepatocellular carcinoma progression via modulation of SHP1-regulated STAT3/HMGA2 signaling axis.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Dec 2;20(15):6281-6296. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.99683. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39664573 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Pro-resolving and Pro-efferocytic Nanoparticles for Atherosclerosis Therapy.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Sep 13;7(10):3086-3095. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00292. eCollection 2024 Oct 11. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 39416959
-
The regulation of cGAS-STING signaling by RNA virus-derived components.Virol J. 2024 May 1;21(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02359-1. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 38693578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Natural Products in the Treatment of Retinopathy of Prematurity: Exploring Therapeutic Potentials.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 2;25(15):8461. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158461. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39126030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

