Recombinant Phytase Modulates Blood Amino Acids and Proteomics Profiles in Pigs Fed with Low-Protein, -Calcium, and -Phosphorous Diets
- PMID: 38203511
- PMCID: PMC10778770
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010341
Recombinant Phytase Modulates Blood Amino Acids and Proteomics Profiles in Pigs Fed with Low-Protein, -Calcium, and -Phosphorous Diets
Abstract
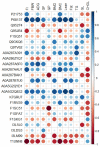
A beneficial effect of corn-expressed phytase (CEP) on the growth performance of pigs fed with very low-protein (VLP) diets was previously shown. Little is known whether this improvement is related to alterations in the expression profiles of blood proteins and amino acids (AAs). The objective of this study was to investigate whether supplementation of VLP, low-calcium (Ca), and low-P diets with a CEP would alter the blood AAs and protein expression profiles in pigs. Forty-eight pigs were subjected to one of the following groups (n = 8/group) for 4 weeks: positive control (PC), negative control-reduced protein (NC), NC + low-dose CEP (LD), NC + high-dose CEP (HD), LD with reduced Ca/P (LDR), and HD with reduced Ca/P (HDR). Plasma leucine and phenylalanine concentrations were reduced in NC; however, the LD diet recovered the concentration of these AAs. Serum proteomics analysis revealed that proteins involved with growth regulation, such as selenoprotein P were upregulated while the IGF-binding proteins family proteins were differentially expressed in CEP-supplemented groups. Furthermore, a positive correlation was detected between growth and abundance of proteins involved in bone mineralization and muscle structure development. Taken together, CEP improved the blood profile of some essential AAs and affected the expression of proteins involved in the regulation of growth.
Keywords: corn-expressed phytase; low-protein diet; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of a novel corn-expressed E. coli phytase on digestibility of calcium and phosphorous, growth performance, and bone ash in young growing pigs1.J Anim Sci. 2019 Jul 30;97(8):3390-3398. doi: 10.1093/jas/skz190. J Anim Sci. 2019. PMID: 31162527 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Corn-Expressed Phytase Improves Daily Weight Gain, Protein Efficiency Ratio and Nutrients Digestibility and Alters Fecal Microbiota in Pigs Fed with Very Low Protein Diets.Animals (Basel). 2020 Oct 20;10(10):1926. doi: 10.3390/ani10101926. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33092137 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of low doses of Aspergillus niger phytase on growth performance, bone strength, and nutrient absorption and excretion by growing and finishing swine fed corn-soybean meal diets deficient in available phosphorus and calcium.J Anim Sci. 2008 Apr;86(4):858-70. doi: 10.2527/jas.2007-0312. Epub 2007 Dec 21. J Anim Sci. 2008. PMID: 18156343
-
Effect of reduced dietary calcium concentration and phytase supplementation on calcium and phosphorus utilization in weanling pigs with modified mineral status.J Anim Sci. 2010 May;88(5):1706-17. doi: 10.2527/jas.2008-1615. Epub 2010 Jan 29. J Anim Sci. 2010. PMID: 20118415 Clinical Trial.
-
Growth performance, diet nutrient digestibility, and bone mineralization in weaned pigs fed pelleted diets containing thermostable phytase.J Anim Sci. 2013 Feb;91(2):745-54. doi: 10.2527/jas.2011-4949. Epub 2012 Nov 12. J Anim Sci. 2013. PMID: 23148255 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- National Research Council . Nutrient Requirements of Swine. 11th Revised ed. National Academies Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2012.
-
- Yue L.Y., Qiao S.Y. Effects of low-protein diets supplemented with crystalline amino acids on performance and intestinal development in piglets over the first 2 weeks after weaning. Livest. Sci. 2008;115:144–152. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2007.06.018. - DOI
-
- Manjarin R., Zamora V., Wu G., Steibel J.P., Kirkwood R.N., Taylor N.P., Wils-Plotz E., Trifilo K., Trottier N.L. Effect of amino acids supply in reduced crude protein diets on performance, efficiency of mammary uptake, and transporter gene expression in lactating sows. J. Anim. Sci. 2012;90:3088–3100. doi: 10.2527/jas.2011-4338. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

