COPI Vesicle Disruption Inhibits Mineralization via mTORC1-Mediated Autophagy
- PMID: 38203512
- PMCID: PMC10779376
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010339
COPI Vesicle Disruption Inhibits Mineralization via mTORC1-Mediated Autophagy
Abstract
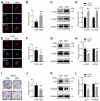
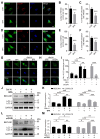
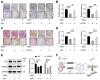
Bone mineralization is a sophisticated regulated process composed of crystalline calcium phosphate and collagen fibril. Autophagy, an evolutionarily conserved degradation system, whereby double-membrane vesicles deliver intracellular macromolecules and organelles to lysosomes for degradation, has recently been shown to play an essential role in mineralization. However, the formation of autophagosomes in mineralization remains to be determined. Here, we show that Coat Protein Complex I (COPI), responsible for Golgi-to-ER transport, plays a pivotal role in autophagosome formation in mineralization. COPI vesicles were increased after osteoinduction, and COPI vesicle disruption impaired osteogenesis. Mechanistically, COPI regulates autophagy activity via the mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway, a key regulator of autophagy. Inhibition of mTOR1 rescues the impaired osteogenesis by activating autophagy. Collectively, our study highlights the functional importance of COPI in mineralization and identifies COPI as a potential therapeutic target for treating bone-related diseases.
Keywords: COPI vesicle; autophagy; mineralization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reconstitution of COPI Vesicle and Tubule Formation.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1496:63-74. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6463-5_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27632002 Free PMC article.
-
ArfGAP1 activity and COPI vesicle biogenesis.Traffic. 2009 Mar;10(3):307-15. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2008.00865.x. Epub 2008 Dec 4. Traffic. 2009. PMID: 19055691
-
Early endosomes and endosomal coatomer are required for autophagy.J Cell Biol. 2009 Apr 20;185(2):305-21. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200810098. Epub 2009 Apr 13. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19364919 Free PMC article.
-
Physical aspects of COPI vesicle formation.Mol Membr Biol. 2010 Nov;27(8):428-42. doi: 10.3109/09687688.2010.510485. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Mol Membr Biol. 2010. PMID: 21067455 Review.
-
Skeletal and dental tissue mineralization: The potential role of the endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi complex and the endolysosomal and autophagic transport systems.Bone. 2025 Apr;193:117390. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2025.117390. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Bone. 2025. PMID: 39814250 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Autophagy in the Mineralization Process of Bone and Dentin.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 29;26(13):6278. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136278. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-372-3p represses hepatic stellate cell activation via the RhoC/ROCK pathway.Cytotechnology. 2025 Apr;77(2):60. doi: 10.1007/s10616-025-00715-9. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Cytotechnology. 2025. PMID: 39959789
-
Golgiphagy: a novel selective autophagy to the fore.Cell Biosci. 2024 Oct 22;14(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01311-8. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39438975 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 82170927/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 2022JC-57/Outstanding Youth Science Foundation Project of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology
- sxtr042021004/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Xi'an Jiaotong University
- 2023-JC-QN-0842/the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

