Cis-Regulatory Elements in Mammals
- PMID: 38203513
- PMCID: PMC10779164
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010343
Cis-Regulatory Elements in Mammals
Abstract
In cis-regulatory elements, enhancers and promoters with complex molecular interactions are used to coordinate gene transcription through physical proximity and chemical modifications. These processes subsequently influence the phenotypic characteristics of an organism. An in-depth exploration of enhancers and promoters can substantially enhance our understanding of gene regulatory networks, shedding new light on mammalian development, evolution and disease pathways. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of the intrinsic structural attributes, detection methodologies as well as the operational mechanisms of enhancers and promoters, coupled with the relevant novel and innovative investigative techniques used to explore their actions. We further elucidated the state-of-the-art research on the roles of enhancers and promoters in the realms of mammalian development, evolution and disease, and we conclude with forward-looking insights into prospective research avenues.
Keywords: cis-regulatory elements; enhancers; mammals; promoters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
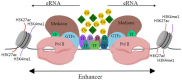
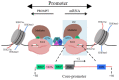
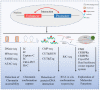
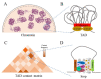
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 32102514/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- U20A2051/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31972996/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020GXNSFBA297148/Guangxi Natural Science Foundation
- SKLCUSA-a202203/State Key Laboratory for Conservation and Utilization of Subtropical Agro-Bioresources
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

