Nucleotide, Phospholipid, and Kynurenine Metabolites Are Robustly Associated with COVID-19 Severity and Time of Plasma Sample Collection in a Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 38203516
- PMCID: PMC10779247
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010346
Nucleotide, Phospholipid, and Kynurenine Metabolites Are Robustly Associated with COVID-19 Severity and Time of Plasma Sample Collection in a Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
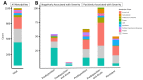
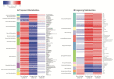
Understanding the molecular underpinnings of disease severity and progression in human studies is necessary to develop metabolism-related preventative strategies for severe COVID-19. Metabolites and metabolic pathways that predispose individuals to severe disease are not well understood. In this study, we generated comprehensive plasma metabolomic profiles in >550 patients from the Longitudinal EMR and Omics COVID-19 Cohort. Samples were collected before (n = 441), during (n = 86), and after (n = 82) COVID-19 diagnosis, representing 555 distinct patients, most of which had single timepoints. Regression models adjusted for demographics, risk factors, and comorbidities, were used to determine metabolites associated with predisposition to and/or persistent effects of COVID-19 severity, and metabolite changes that were transient/lingering over the disease course. Sphingolipids/phospholipids were negatively associated with severity and exhibited lingering elevations after disease, while modified nucleotides were positively associated with severity and had lingering decreases after disease. Cytidine and uridine metabolites, which were positively and negatively associated with COVID-19 severity, respectively, were acutely elevated, reflecting the particular importance of pyrimidine metabolism in active COVID-19. This is the first large metabolomics study using COVID-19 plasma samples before, during, and/or after disease. Our results lay the groundwork for identifying putative biomarkers and preventive strategies for severe COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19 severity; biomarkers; longitudinal cohort; phospholipid metabolism; prospective sampling; pyrimidine metabolism; regression analysis; tryptophan metabolism; untargeted metabolomics.
Conflict of interest statement
J.L.-S. is a scientific advisor to Precion, Inc. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . COVID Data Tracker. US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; Atlanta, GA, USA: [(accessed on 19 September 2023)]. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#datatracker-home.
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. WHO Health Emergency Dashboard; Geneva, Switzerland: [(accessed on 19 September 2023)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Costanzo M., De Giglio M.A.R., Roviello G.N. Anti-coronavirus vaccines: Past investigations on SARS-CoV-1 and MERS-CoV, the approved vaccines from BioNTech/Pfizer, Moderna, Oxford/AstraZeneca and others under development against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021;29:4–18. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210521164809. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Costanzo M., De Giglio M.A.R., Roviello G.N. SARS-CoV-2: Recent reports on antiviral therapies based on Lopinavir/Ritonavir, Darunavir/Umifenovir, Hydroxychloroquine, Remdesivir, Favipiravir and other drugs for the treatment of the new coronavirus. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020;27:4536–4541. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666200416131117. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

