Harnessing ADAR-Mediated Site-Specific RNA Editing in Immune-Related Disease: Prediction and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 38203521
- PMCID: PMC10779106
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010351
Harnessing ADAR-Mediated Site-Specific RNA Editing in Immune-Related Disease: Prediction and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
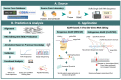
ADAR (Adenosine Deaminases Acting on RNA) proteins are a group of enzymes that play a vital role in RNA editing by converting adenosine to inosine in RNAs. This process is a frequent post-transcriptional event observed in metazoan transcripts. Recent studies indicate widespread dysregulation of ADAR-mediated RNA editing across many immune-related diseases, such as human cancer. We comprehensively review ADARs' function as pattern recognizers and their capability to contribute to mediating immune-related pathways. We also highlight the potential role of site-specific RNA editing in maintaining homeostasis and its relationship to various diseases, such as human cancers. More importantly, we summarize the latest cutting-edge computational approaches and data resources for predicting and analyzing RNA editing sites. Lastly, we cover the recent advancement in site-directed ADAR editing tool development. This review presents an up-to-date overview of ADAR-mediated RNA editing, how site-specific RNA editing could potentially impact disease pathology, and how they could be harnessed for therapeutic applications.
Keywords: ADAR; RNA editing; computational resources; immune-related disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

