Beta Blockade Prevents Cardiac Morphological and Molecular Remodelling in Experimental Uremia
- PMID: 38203544
- PMCID: PMC10778728
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010373
Beta Blockade Prevents Cardiac Morphological and Molecular Remodelling in Experimental Uremia
Abstract
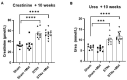
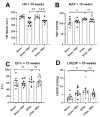
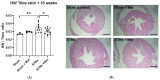
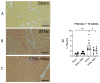
Heart failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD) share several mediators of cardiac pathological remodelling. Akin to heart failure, this remodelling sets in motion a vicious cycle of progressive pathological hypertrophy and myocardial dysfunction in CKD. Several decades of heart failure research have shown that beta blockade is a powerful tool in preventing cardiac remodelling and breaking this vicious cycle. This phenomenon remains hitherto untested in CKD. Therefore, we set out to test the hypothesis that beta blockade prevents cardiac pathological remodelling in experimental uremia. Wistar rats had subtotal nephrectomy or sham surgery and were followed up for 10 weeks. The animals were randomly allocated to the beta blocker metoprolol (10 mg/kg/day) or vehicle. In vivo and in vitro cardiac assessments were performed. Cardiac tissue was extracted, and protein expression was quantified using immunoblotting. Histological analyses were performed to quantify myocardial fibrosis. Beta blockade attenuated cardiac pathological remodelling in nephrectomised animals. The echocardiographic left ventricular mass and the heart weight to tibial length ratio were significantly lower in nephrectomised animals treated with metoprolol. Furthermore, beta blockade attenuated myocardial fibrosis associated with subtotal nephrectomy. In addition, the Ca++- calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CAMKII) pathway was shown to be activated in uremia and attenuated by beta blockade, offering a potential mechanism of action. In conclusion, beta blockade attenuated hypertrophic signalling pathways and ameliorated cardiac pathological remodelling in experimental uremia. The study provides a strong scientific rationale for repurposing beta blockers, a tried and tested treatment in heart failure, for the benefit of patients with CKD.
Keywords: CKD; beta blocker; cardiac remodelling; uremia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


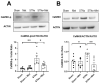
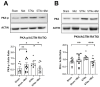
References
-
- Dubin R.F., Deo R., Bansal N., Anderson A.H., Yang P., Go A.S., Keane M., Townsend R., Porter A., Budoff M., et al. Associations of Conventional Echocardiographic Measures with Incident Heart Failure and Mortality: The Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017;12:60–68. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02700316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- System USRD . 2020 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

