Extracellular Vesicles in Atherosclerosis: State of the Art
- PMID: 38203558
- PMCID: PMC10779125
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010388
Extracellular Vesicles in Atherosclerosis: State of the Art
Abstract
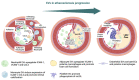
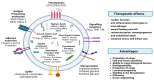
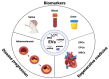
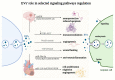
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory disease driven by lipid accumulation in the arteries, leading to narrowing and thrombosis that causes mortality. Emerging evidence has confirmed that atherosclerosis affects younger people and is involved in the majority of deaths worldwide. EVs are associated with critical steps in atherosclerosis, cholesterol metabolism, immune response, endothelial dysfunction, vascular inflammation, and remodeling. Endothelial cell-derived EVs can interact with platelets and monocytes, thereby influencing endothelial dysfunction, atherosclerotic plaque destabilization, and the formation of thrombus. EVs are potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in atherosclerosis (AS) and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Importantly, EVs derived from stem/progenitor cells are essential mediators of cardiogenesis and cardioprotection and may be used in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
Keywords: CVD; EPC; MSC; atherosclerosis; endothelial cells; extracellular vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

