Valproic Acid in Pregnancy Revisited: Neurobehavioral, Biochemical and Molecular Changes Affecting the Embryo and Fetus in Humans and in Animals: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 38203562
- PMCID: PMC10779436
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010390
Valproic Acid in Pregnancy Revisited: Neurobehavioral, Biochemical and Molecular Changes Affecting the Embryo and Fetus in Humans and in Animals: A Narrative Review
Abstract
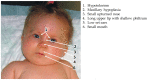
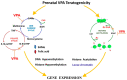
Valproic acid (VPA) is a very effective anticonvulsant and mood stabilizer with relatively few side effects. Being an epigenetic modulator, it undergoes clinical trials for the treatment of advanced prostatic and breast cancer. However, in pregnancy, it seems to be the most teratogenic antiepileptic drug. Among the proven effects are congenital malformations in about 10%. The more common congenital malformations are neural tube defects, cardiac anomalies, urogenital malformations including hypospadias, skeletal malformations and orofacial clefts. These effects are dose related; daily doses below 600 mg have a limited teratogenic potential. VPA, when added to other anti-seizure medications, increases the malformations rate. It induces malformations even when taken for indications other than epilepsy, adding to the data that epilepsy is not responsible for the teratogenic effects. VPA increases the rate of neurodevelopmental problems causing reduced cognitive abilities and language impairment. It also increases the prevalence of specific neurodevelopmental syndromes like autism (ASD) and Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). High doses of folic acid administered prior to and during pregnancy might alleviate some of the teratogenic effect of VPA and other AEDs. Several teratogenic mechanisms are proposed for VPA, but the most important mechanisms seem to be its effects on the metabolism of folate, SAMe and histones, thus affecting DNA methylation. VPA crosses the human placenta and was found at higher concentrations in fetal blood. Its concentrations in milk are low, therefore nursing is permitted. Animal studies generally recapitulate human data.
Keywords: autism; neural tube defects; teratogenic antiepileptic drug; valproic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Valproic acid in pregnancy: how much are we endangering the embryo and fetus?Reprod Toxicol. 2009 Jul;28(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2009.02.014. Epub 2009 Mar 13. Reprod Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19490988 Review.
-
Teratogenicity of valproic acid and its constitutional isomer, amide derivative valnoctamide in mice.Birth Defects Res. 2019 Aug 15;111(14):1013-1023. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1406. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Birth Defects Res. 2019. PMID: 30325584
-
Teratogenicity of sodium valproate.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2005 Mar;4(2):345-53. doi: 10.1517/14740338.4.2.345. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2005. PMID: 15794725 Review.
-
Alteration of embryonic folate metabolism by valproic acid during organogenesis: implications for mechanism of teratogenesis.Neurology. 1992 Apr;42(4 Suppl 5):17-24. Neurology. 1992. PMID: 1574172
-
Influence of the MTHFR genotype on the rate of malformations following exposure to antiepileptic drugs in utero.Eur J Med Genet. 2007 Nov-Dec;50(6):411-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2007.08.002. Epub 2007 Sep 11. Eur J Med Genet. 2007. PMID: 17951123
Cited by
-
Developmental exposure of antibiotics shortens life span and induces teratogenicity in Drosophila melanogaster.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Oct 22;13:101784. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101784. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39534686 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to anti-seizure medication during pregnancy and the risk of autism and ADHD in offspring: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1440145. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1440145. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39105059 Free PMC article.
-
Valproate-Autism Labyrinth.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Aug 19;54(4):131-133. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 39263199
-
Animal Models of Autistic-like Behavior in Rodents: A Scoping Review and Call for a Comprehensive Scoring System.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 28;25(19):10469. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910469. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408797 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro models of valproic acid to assess neurodevelopmental toxicity: A scoping review.Epilepsia. 2025 Jul;66(7):2170-2181. doi: 10.1111/epi.18392. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Epilepsia. 2025. PMID: 40152543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnon J., Shechtman S., Ornoy A. The use of psychiatric drugs in pregnancy and lactation. Isr. J. Psychiatry Relat. Sci. 2000;37:205–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

