Synovial Fluid from Patients with Osteoarthritis Shows Different Inflammatory Features Depending on the Presence of Calcium Pyrophosphate Crystals
- PMID: 38203564
- PMCID: PMC10778695
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010393
Synovial Fluid from Patients with Osteoarthritis Shows Different Inflammatory Features Depending on the Presence of Calcium Pyrophosphate Crystals
Abstract
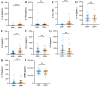
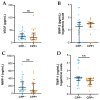
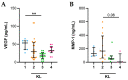
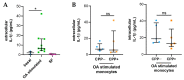
The role of calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) crystals in osteoarthritis (OA) is still a matter of debate. With this study we aimed to investigate the inflammatory features of synovial fluid (SF) collected from patients with OA with CPP crystals compared with those without crystals. We also explored the effect of OA SF on monocytes response. SFs were collected from adult patients with OA and subdivided according to the presence of crystals. Local cellular and humoral inflammatory mediators were analysed in the SF samples. The expression levels of IL-1β, IL-18, CASP-1, NLRP3, and GAPDH were measured by RT-PCR in the cells obtained by pelleting the SF samples. For the in vitro study, a monocytic cell line was treated with selected SF samples. SF with CPP crystals showed a significant increase in inflammatory cellular indices and higher levels of IL-1β, IL-8, and caspase-1 transcript with respect to SF without crystals. Higher concentrations of VEGF were also observed in the early stages of the whole OA patients. THP-1 cells stimulated with OA SF released a significant amount of IL-1 β in culture supernatants. This study demonstrated that SF collected from patients with OA shows different inflammatory features depending on the presence of CPP crystals.
Keywords: calcium pyrophosphate crystals; inflammation; interleukin-1; osteoarthritis; synovial fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of Calcium Crystals in Knee Osteoarthritis Synovial Fluid: A Comparison Between Polarized Light and Scanning Electron Microscopy.J Clin Rheumatol. 2016 Oct;22(7):369-71. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000000416. J Clin Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27660935
-
Prevalence of calcium pyrophosphate and monosodium urate crystals in synovial fluid of patients with previously diagnosed joint diseases.Joint Bone Spine. 2013 May;80(3):287-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2012.08.006. Epub 2012 Sep 26. Joint Bone Spine. 2013. PMID: 23021157
-
Interplay of calcium pyrophosphate crystals, oxidative stress, and clinical features on knee osteoarthritis severity.Clin Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;44(1):433-441. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07220-y. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Clin Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39503904
-
Calcium-Containing Crystals and Osteoarthritis: an Unhealthy Alliance.Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018 Mar 8;20(3):13. doi: 10.1007/s11926-018-0721-9. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29516278 Review.
-
The role of calcium crystals and their effect on osteoarthritis pathogenesis.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2021 Dec;35(4):101722. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2021.101722. Epub 2021 Oct 31. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2021. PMID: 34732285 Review.
Cited by
-
Predominance of Calcium Pyrophosphate Crystals in Synovial Fluid Samples of Patients at a Large Tertiary Center.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;15(7):907. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15070907. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218257 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphate in Physiological and Pathological Mineralization: Important yet Often Unheeded.MedComm (2020). 2025 Jul 13;6(7):e70298. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70298. eCollection 2025 Jul. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40661139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in nanocrystals for arthritis drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2025 Jul;22(7):1031-1042. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2025.2505758. Epub 2025 May 31. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 40357685 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Krakowski P., Karpiński R., Maciejewski R., Jonak J., Jurkiewicz A. Short-Term Effects of Arthroscopic Microfracturation of Knee Chondral Defects in Osteoarthritis. Appl. Sci. 2020;10:8312. doi: 10.3390/app10238312. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

