Synovial Fluid from Patients with Osteoarthritis Shows Different Inflammatory Features Depending on the Presence of Calcium Pyrophosphate Crystals
- PMID: 38203564
- PMCID: PMC10778695
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010393
Synovial Fluid from Patients with Osteoarthritis Shows Different Inflammatory Features Depending on the Presence of Calcium Pyrophosphate Crystals
Abstract
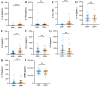
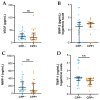
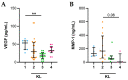
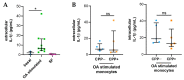
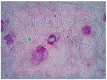
The role of calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) crystals in osteoarthritis (OA) is still a matter of debate. With this study we aimed to investigate the inflammatory features of synovial fluid (SF) collected from patients with OA with CPP crystals compared with those without crystals. We also explored the effect of OA SF on monocytes response. SFs were collected from adult patients with OA and subdivided according to the presence of crystals. Local cellular and humoral inflammatory mediators were analysed in the SF samples. The expression levels of IL-1β, IL-18, CASP-1, NLRP3, and GAPDH were measured by RT-PCR in the cells obtained by pelleting the SF samples. For the in vitro study, a monocytic cell line was treated with selected SF samples. SF with CPP crystals showed a significant increase in inflammatory cellular indices and higher levels of IL-1β, IL-8, and caspase-1 transcript with respect to SF without crystals. Higher concentrations of VEGF were also observed in the early stages of the whole OA patients. THP-1 cells stimulated with OA SF released a significant amount of IL-1 β in culture supernatants. This study demonstrated that SF collected from patients with OA shows different inflammatory features depending on the presence of CPP crystals.
Keywords: calcium pyrophosphate crystals; inflammation; interleukin-1; osteoarthritis; synovial fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Krakowski P., Karpiński R., Maciejewski R., Jonak J., Jurkiewicz A. Short-Term Effects of Arthroscopic Microfracturation of Knee Chondral Defects in Osteoarthritis. Appl. Sci. 2020;10:8312. doi: 10.3390/app10238312. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

