Molecular Characteristics and Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus Exotoxins
- PMID: 38203566
- PMCID: PMC10778951
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010395
Molecular Characteristics and Pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus Exotoxins
Abstract
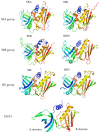
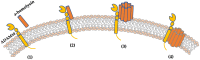
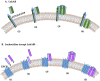
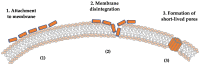
Staphylococcus aureus stands as one of the most pervasive pathogens given its morbidity and mortality worldwide due to its roles as an infectious agent that causes a wide variety of diseases ranging from moderately severe skin infections to fatal pneumonia and sepsis. S. aureus produces a variety of exotoxins that serve as important virulence factors in S. aureus-related infectious diseases and food poisoning in both humans and animals. For example, staphylococcal enterotoxins (SEs) produced by S. aureus induce staphylococcal foodborne poisoning; toxic shock syndrome toxin-1 (TSST-1), as a typical superantigen, induces toxic shock syndrome; hemolysins induce cell damage in erythrocytes and leukocytes; and exfoliative toxin induces staphylococcal skin scalded syndrome. Recently, Panton-Valentine leucocidin, a cytotoxin produced by community-associated methicillin-resistant S. aureus (CA-MRSA), has been reported, and new types of SEs and staphylococcal enterotoxin-like toxins (SEls) were discovered and reported successively. This review addresses the progress of and novel insights into the molecular structure, biological activities, and pathogenicity of both the classic and the newly identified exotoxins produced by S. aureus.
Keywords: Panton–Valentine leucocidin; exfoliative toxin; hemolysin; membrane-damaging toxin; staphylococcal enterotoxin; superantigen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Virulence determinants in community and hospital meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.J Hosp Infect. 2007 Jun;65 Suppl 2:105-9. doi: 10.1016/S0195-6701(07)60025-5. J Hosp Infect. 2007. PMID: 17540252 Review.
-
First Genome-Based Characterisation and Staphylococcal Enterotoxin Production Ability of Methicillin-Susceptible and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strains Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Foods in Algiers (Algeria).Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 25;14(11):731. doi: 10.3390/toxins14110731. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355981 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging threat of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) clone ST22-PT, carrying both Panton-Valentine leucocidin and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 genes.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023 Apr 3;78(4):1023-1027. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkad039. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023. PMID: 36814074
-
Molecular characteristics of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Hokkaido, northern main island of Japan: identification of sequence types 6 and 59 Panton-Valentine leucocidin-positive community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Microb Drug Resist. 2011 Jun;17(2):241-50. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2010.0136. Epub 2011 Mar 13. Microb Drug Resist. 2011. PMID: 21395449
-
Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000 Jan;13(1):16-34, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/CMR.13.1.16. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000. PMID: 10627489 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Composite Films Based on Linear Polyethyleneimine Polymer and Starch or Polysaccharides from DDGS: Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Studies.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Feb 9;17(4):458. doi: 10.3390/polym17040458. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006120 Free PMC article.
-
Lung function and the risk of Parkinson's disease: a population-based cohort study.J Neurol. 2025 Jul 26;272(8):538. doi: 10.1007/s00415-025-13274-y. J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40715805
-
Small molecule antipathogenic agents against Staphylococcus aureus infections.RSC Med Chem. 2025 Jul 18. doi: 10.1039/d5md00272a. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40756523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KLF4 promotes cisplatin resistance by activating mTORC1 signaling in ovarian cancer.Discov Oncol. 2024 Nov 20;15(1):682. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01576-y. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39565445 Free PMC article.
-
Chrysanthemum zawadskii var. latilobum Flower Essential Oil Reduces MRSA Pathogenicity by Inhibiting Virulence Gene Expression.Molecules. 2025 Jan 25;30(3):553. doi: 10.3390/molecules30030553. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39942657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu D.L., Li S., Fang R., Ono H.K. Update on molecular diversity and multipathogenicity of staphylococcal superantigen toxins. Anim. Dis. 2021;1:7. doi: 10.1186/s44149-021-00007-7. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

