Aquaporin Expression and Regulation in Clinical and Experimental Sepsis
- PMID: 38203657
- PMCID: PMC10778766
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010487
Aquaporin Expression and Regulation in Clinical and Experimental Sepsis
Abstract
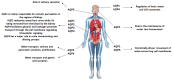
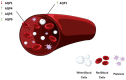
Sepsis is an inflammatory disorder caused by the host's dysfunctional response to infection. Septic patients present diverse clinical characteristics, and in the recent years, it has been the main cause of death in intensive care units (ICU). Aquaporins, membrane proteins with a role in water transportation, have been reported to participate in numerous biological processes. Their role in sepsis progression has been studied extensively. This review aims to examine recent literature on aquaporin expression and regulation in clinical sepsis, as well as established experimental models of sepsis. We will present how sepsis affects aquaporin expression at the molecular and protein level. Moreover, we will delve into the importance of aquaporin regulation at transcriptional, post-transcriptional, translational, and post-translational levels in sepsis by presenting data on aquaporin regulation by non-coding RNAs and selected chemical molecules. Finally, we will focus on the importance of aquaporin single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the setting of sepsis.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; aquaporin; lnRNA; miRNA; sepsis; single-nucleotide polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Induced expression and functional effects of aquaporin-1 in human leukocytes in sepsis.Crit Care. 2013 Sep 12;17(5):R199. doi: 10.1186/cc12893. Crit Care. 2013. PMID: 24028651 Free PMC article.
-
The Aquaporin 3 Polymorphism (rs17553719) Is Associated with Sepsis Survival and Correlated with IL-33 Secretion.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 23;25(3):1400. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031400. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338680 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis Care Pathway 2019.Qatar Med J. 2019 Nov 7;2019(2):4. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2019.qccc.4. eCollection 2019. Qatar Med J. 2019. PMID: 31763206 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms and regulation of the gene-expression response to sepsis.Pediatrics. 2010 Jun;125(6):1248-58. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-3274. Epub 2010 May 17. Pediatrics. 2010. PMID: 20478944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The aquaporins.Genome Biol. 2006;7(2):206. doi: 10.1186/gb-2006-7-2-206. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Genome Biol. 2006. PMID: 16522221 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aquaporins in sepsis- an update.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 31;15:1495206. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1495206. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39544938 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methazolamide Reduces the AQP5 mRNA Expression and Immune Cell Migration-A New Potential Drug in Sepsis Therapy?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 3;25(1):610. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010610. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38203778 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Aquaporins in Human Studies: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential in Critical Illness.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;14(12):1688. doi: 10.3390/life14121688. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pilot study on the potential of low-salt brine with oregano essential oil for post-preservation of white brined cheese.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 1;15(1):28151. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-13384-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40750643 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Markou A., Unger L., Abir-Awan M., Saadallah A., Halsey A., Balklava Z., Conner M., Tornroth-Horsefield S., Greenhill S.D., Conner A., et al. Molecular mechanisms governing aquaporin relocalisation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2022;1864:183853. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183853. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

