Non-Coding RNAs as Key Regulators in Lung Cancer
- PMID: 38203731
- PMCID: PMC10778604
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010560
Non-Coding RNAs as Key Regulators in Lung Cancer
Abstract
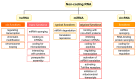
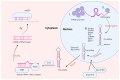
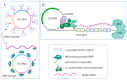
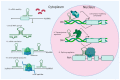
For several decades, most lung cancer investigations have focused on the search for mutations in candidate genes; however, in the last decade, due to the fact that most of the human genome is occupied by sequences that do not code for proteins, much attention has been paid to non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) that perform regulatory functions. In this review, we principally focused on recent studies of the function, regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic potential of ncRNAs including microRNA (miRNA), long ncRNA (lncRNA), and circular RNA (circRNA) in different types of lung cancer.
Keywords: circRNA; lncRNA; lung cancer; miRNA; non-coding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-coding RNA in cancer.Essays Biochem. 2021 Oct 27;65(4):625-639. doi: 10.1042/EBC20200032. Essays Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33860799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs: key players in cardiac disease.J Physiol. 2020 Jul;598(14):2995-3003. doi: 10.1113/JP278131. Epub 2019 Jul 26. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31291008 Review.
-
A comprehensive review of web-based resources of non-coding RNAs for plant science research.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 May 22;14(8):819-832. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.24593. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29989090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of selected non-coding RNAs in the biology of non-small cell lung cancer.Adv Med Sci. 2023 Mar;68(1):121-137. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2023.02.004. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Adv Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36933328 Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs in Kawasaki disease: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications.Bioessays. 2022 Jun;44(6):e2100256. doi: 10.1002/bies.202100256. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Bioessays. 2022. PMID: 35355301 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in the abscopal effect: bridging radiotherapy and systemic anti-tumor immunity for enhanced cancer therapy.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2025 Aug 13;42(5):48. doi: 10.1007/s10585-025-10364-z. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2025. PMID: 40797149 Review.
-
Downregulation of hsa_circTLK1 represses non-small cell lung cancer progression by regulating miR-876-3p/SRSF7 axis.Heliyon. 2024 May 25;10(11):e31972. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31972. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38868058 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the development and progression of long non-coding RNA in upper gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma.Discov Oncol. 2025 Jun 1;16(1):980. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02800-z. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40450604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modifications in early stage lung cancer: pathogenesis, biomarkers, and early diagnosis.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 21;6(3):e70080. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70080. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 39991629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The NcRNA/Wnt axis in lung cancer: oncogenic mechanisms, remarkable indicators and therapeutic targets.J Transl Med. 2025 Mar 14;23(1):326. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06326-4. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40087753 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

