Breg-Mediated Immunoregulation in the Skin
- PMID: 38203754
- PMCID: PMC10778726
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010583
Breg-Mediated Immunoregulation in the Skin
Abstract
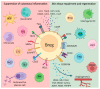
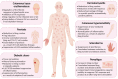
Wound healing is a complex process involving a coordinated series of events aimed at restoring tissue integrity and function. Regulatory B cells (Bregs) are a subset of B lymphocytes that play an essential role in fine-tuning immune responses and maintaining immune homeostasis. Recent studies have suggested that Bregs are important players in cutaneous immunity. This review summarizes the current understanding of the role of Bregs in skin immunity in health and pathology, such as diabetes, psoriasis, systemic sclerosis, cutaneous lupus erythematosus, cutaneous hypersensitivity, pemphigus, and dermatomyositis. We discuss the mechanisms by which Bregs maintain tissue homeostasis in the wound microenvironment through the promotion of angiogenesis, suppression of effector cells, and induction of regulatory immune cells. We also mention the potential clinical applications of Bregs in promoting wound healing, such as the use of adoptive Breg transfer.
Keywords: immune regulation; inflammatory skin pathology; regulatory B cells; skin homeostasis; tissue regeneration; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chiricozzi A., Zhang S., Dattola A., Cannizzaro M.V., Gabellini M., Chimenti S., Nistico S.P. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Cutaneous Autoimmune Disorders. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 2012;26:165–170. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

