HCC-Related lncRNAs: Roles and Mechanisms
- PMID: 38203767
- PMCID: PMC10779127
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010597
HCC-Related lncRNAs: Roles and Mechanisms
Abstract
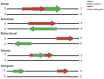
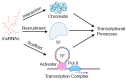
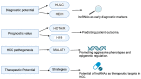
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presents a significant global health threat, particularly in regions endemic to hepatitis B and C viruses, and because of the ongoing pandemic of obesity causing metabolic-dysfunction-related fatty liver disease (MAFLD), a precursor to HCC. The molecular intricacies of HCC, genetic and epigenetic alterations, and dysregulated signaling pathways facilitate personalized treatment strategies based on molecular profiling. Epigenetic regulation, encompassing DNA methyltion, histone modifications, and noncoding RNAs, functions as a critical layer influencing HCC development. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are spotlighted for their diverse roles in gene regulation and their potential as diagnostic and therapeutic tools in cancer. In this review, we explore the pivotal role of lncRNAs in HCC, including MAFLD and viral hepatitis, the most prevalent risk factors for hepatocarcinogenesis. The dysregulation of lncRNAs is implicated in HCC progression by modulating chromatin regulation and transcription, sponging miRNAs, and influencing structural functions. The ongoing studies on lncRNAs contribute to a deeper comprehension of HCC pathogenesis and offer promising routes for precision medicine, highlighting the utility of lncRNAs as early biomarkers, prognostic indicators, and therapeutic targets.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; long noncoding RNA; prognosis; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

