The Influence of Genetic Polymorphisms on the Expression of Interleukin-1beta, Prostaglandin E2 and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Peri-Implant Crevicular Fluid: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 38203822
- PMCID: PMC10779319
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25010651
The Influence of Genetic Polymorphisms on the Expression of Interleukin-1beta, Prostaglandin E2 and Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Peri-Implant Crevicular Fluid: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
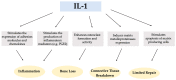
The aim of this study was to evaluate the possible relationships between polymorphisms in the interleukin-1 (IL-1) A, IL-1B, and IL-1RN genes and concentrations of the inflammatory mediators IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in peri-implant crevicular fluid (PICF). A cross-sectional analytical study was conducted on 51 patients with dental implants. Samples from the buccal mucosa were obtained, and genetic analysis was performed using the real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique for IL-1A and IL-1B and PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis for IL-1RN. For the biochemical analysis, the concentrations of IL-1β and TNF-α were analyzed using multiplexed fluorescent sphere immunoassays, and PGE2 by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. In patients with detected IL-1RN polymorphism, there was an increase in the concentration of the three mediators with statistically significant differences in the mean values of TNF-α and PGE2, regardless of peri-implant health status (p = 0.002 and p = 0.049, respectively). The concentrations of all three mediators were positively and significantly correlated (IL-1β vs. TNF-α Rho = 0.480, p < 0.001; IL-1β vs. PGE2 Rho = 0.382, p = 0.006; and TNF-α vs. PGE2 Rho = 0.528, p < 0.001). We can conclude that the IL-1RN polymorphism exerts an influence on the PICF immune response, which may explain the influence of this genetic polymorphism on the occurrence of peri-implantitis.
Keywords: dental implants; genotype; interleukin-1; interleukin-1alpha; peri-implantitis; polymorphisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations between peri-implant crevicular fluid volume, concentrations of crevicular inflammatory mediators, and composite IL-1A -889 and IL-1B +3954 genotype. A cross-sectional study on implant recall patients with and without clinical signs of peri-implantitis.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007 Apr;18(2):212-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2006.01322.x. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007. PMID: 17348886
-
Analysis of the Association of IL-1A, IL-1B, and IL-1RN Genetic Polymorphisms with Peri-implantitis in a Portuguese Population.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2024 Aug 29;39(4):103-111. doi: 10.11607/jomi.10615. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2024. PMID: 38607354
-
Interleukin-1beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels and neutrophil elastase activity in peri-implant crevicular fluid.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002 Oct;13(5):470-6. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.2002.130505.x. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002. PMID: 12453123
-
Use of IL-1 β, IL-6, TNF-α, and MMP-8 biomarkers to distinguish peri-implant diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019 Feb;21(1):190-207. doi: 10.1111/cid.12694. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 30508312
-
A review of biomarkers in peri-miniscrew implant crevicular fluid (PMICF).Prog Orthod. 2017 Nov 27;18(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40510-017-0195-8. Prog Orthod. 2017. PMID: 29177754 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial dysbiosis in periodontitis and peri-implantitis: pathogenesis, immune responses, and therapeutic.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Feb 11;15:1517154. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1517154. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40007610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Interleukin 37 and its polymorphism (rs3811047) in children with type I diabetes.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 7;52(1):678. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10779-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40622574
-
The Mechanism by Which Estrogen Level Affects Knee Osteoarthritis Pain in Perimenopause and Non-Pharmacological Measures.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 7;26(6):2391. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062391. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141035 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pjetursson B.E., Thoma D., Jung R., Zwahlen M., Zembic A. A Systematic Review of the Survival and Complication Rates of Implant-Supported Fixed Dental Prostheses (FDPs) after a Mean Observation Period of at Least 5 Years. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2012;23((Suppl. S6)):22–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2012.02546.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Berglundh T., Armitage G., Araujo M.G., Avila-Ortiz G., Blanco J., Camargo P.M., Chen S., Cochran D., Derks J., Figuero E., et al. Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions: Consensus Report of Workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018;45((Suppl. S20)):S286–S291. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12957. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases