A multicenter study on efficacy of dual-target neoadjuvant therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer and a consistent analysis of efficacy evaluation of neoadjuvant therapy by Miller-Payne and RCB pathological evaluation systems (CSBrS-026)
- PMID: 38204446
- PMCID: PMC10774131
- DOI: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2023.06.13
A multicenter study on efficacy of dual-target neoadjuvant therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer and a consistent analysis of efficacy evaluation of neoadjuvant therapy by Miller-Payne and RCB pathological evaluation systems (CSBrS-026)
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the factors influencing pathological complete response (pCR) rate in early breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant dual-target [trastuzumab (H) + pertuzumab (P)] therapy combined with chemotherapy. Additionally, the consistency of the Miller-Payne and residual cancer burden (RCB) systems in evaluating the efficacy of neoadjuvant therapy for early human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)+ breast cancer was analyzed.
Methods: The clinicopathological data of female patients with early-stage HER2+ breast cancer who received dual-target neoadjuvant therapy at 26 hospitals of the Chinese Society of Breast Surgery (CSBrS) from March 2019 to December 2021 were collected. Patients were allocated to four groups: the HER2 immunohistochemistry (IHC) 3+/hormone receptor (HR)-, IHC3+/HR+, IHC2+ in situ hybridization (ISH)+/HR- and IHC2+ ISH+/HR+ groups. The overall pCR rate for patients, the pCR rate in each group and the factors affecting the pCR rate were analyzed. The consistency between the Miller-Payne and RCB systems in assessing the efficacy of neoadjuvant therapy was analyzed.
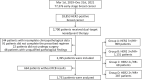
Results: From March 1, 2019, to December 31, 2021, 77,376 female patients with early-stage breast cancer were treated at 26 hospitals; 18,853 (24.4%) of these patients were HER2+. After exclusion of unqualified patients, 2,395 patients who received neoadjuvant dual-target (H+P) therapy combined with chemotherapy were included in this study. The overall pCR rate was 53.0%, and the patients' HR statuses and different HER2+ statuses were significantly correlated with the pCR rate (P<0.05). The consistency of the pathological efficacy assessed by the Miller-Payne and RCB systems was 88.0% (κ=0.717, P<0.001).
Conclusions: Different HER2 expression statuses and HR expression statuses are correlated with the pCR rate after dual-target neoadjuvant therapy in HER2+ breast cancer patients. There is a relatively good consistency between Miller-Payne and RCB systems in evaluating the pathologic efficacy of neoadjuvant therapy for HER2+ breast cancer.
Keywords: Breast cancer; HER2-positive; Miller-Payne system; RCB system; neoadjuvant therapy.
Copyright ©2023 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of residual cancer burden and Miller-Payne system after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer.Gland Surg. 2021 Dec;10(12):3211-3221. doi: 10.21037/gs-21-608. Gland Surg. 2021. PMID: 35070881 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant therapy for early human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive breast cancer in China: A multicenter real-world study (CSBrS-015).Chin Med J (Engl). 2022 Oct 5;135(19):2311-2318. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002197. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022. PMID: 36535009 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical Status Predicts Pathologic Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in HER2-Overexpressing Breast Cancers.Ann Surg Oncol. 2025 Feb;32(2):931-943. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-16470-8. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Ann Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39521739 Free PMC article.
-
Pathologic Complete Response Achieved in Early-Stage HER2-Positive Breast Cancer After Neoadjuvant Therapy With Trastuzumab and Chemotherapy vs. Trastuzumab, Chemotherapy, and Pertuzumab: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials.Cureus. 2023 May 31;15(5):e39780. doi: 10.7759/cureus.39780. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37398703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual HER2 Blockade in Neoadjuvant Treatment of HER2+ Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis and Review.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Jan-Dec;19:1533033820960721. doi: 10.1177/1533033820960721. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2020. PMID: 32990165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The complex interplay of tumor-infiltrating cells in driving therapeutic resistance pathways.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Aug 19;22(1):405. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01776-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39160622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pyrotinib is effective in both trastuzumab-sensitive and primary resistant HER2-positive breast tumors.Chin J Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 30;36(2):124-137. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2024.02.03. Chin J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38751436 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential neoadjuvant chemotherapy using pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by taxanes with complete trastuzumab and pertuzumab treatment for HER2-positive breast cancer: A phase II single-arm study.Chin J Cancer Res. 2024 Feb 29;36(1):55-65. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2024.01.06. Chin J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38455369 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in regional nodal management of early-stage breast cancer.Chin J Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 30;36(2):215-225. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2024.02.08. Chin J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38751438 Free PMC article.
-
HER2-low status improves prognosis prediction in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant treatment: A comparison of pathological stage, modified CPS+EG scoring system, and Neo-Bioscore.Chin J Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 30;36(6):729-741. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2024.06.10. Chin J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39802892 Free PMC article.
References
-
-
NCCN. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Breast Cancer (Version 1.2022). (Version 1.2022). Available online: http://www.nccn.org
-
-
-
Working Committee of the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Guidelines of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology Breast Cancer (CSCO BC) 2022. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2022.
-
-
- Gianni L, Pienkowski T, Im YH, et al 5-year analysis of neoadjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in patients with locally advanced, inflammatory, or early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer (NeoSphere): a multicenter, open-label, phase 2 randomized trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:791–800. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)00163-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shao Z, Pang D, Yang H, et al Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of pertuzumab, trastuzumab, and docetaxel for patients with early or locally advanced ERBB2-positive breast cancer in Asia: The PEONY phase 3 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020;6:e193692. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.3692. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
