Evaluation of cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of different pulp capping liners
- PMID: 38204476
- PMCID: PMC10763819
- DOI: 10.1080/26415275.2023.2287019
Evaluation of cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of different pulp capping liners
Abstract
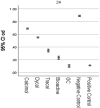
This study compares the cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of five pulp capping liners. This in vitro study was conducted on Fuji II LC glass ionomer, Dycal, Calcimol LC, TheraCal LC, and ACTIVA BioACTIVE. For cytotoxicity, the (MTT) methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium assay was performed on 3 samples from each group of human dental pulp cells (HDPSCs) after 24 h of incubation. The direct contact test (DCT) for antibacterial activity, 6 samples (3 for each material, and 3 for negative control), from each liner were made to evaluate Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans), Lactobacillus casei (L. casei), and Lactobacillus acidophilus (L. acidophilus). Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-hoc test (alpha = 0.05). Data analysis showed that the cytotoxicity of the materials was significantly different (p < 0.001). Fuji II LC and ACTIVA BioACTIVE showed strong cytotoxicity, TheraCal LC moderate cytotoxicity, and Dycal and Calcimol LC slight cytotoxicity. The analysis also revealed a significant difference among the materials regarding antibacterial activity (p < 0.001). Tukey's test showed that the mean percentage of reduction in colony count was significant for all liners compared with the positive control (p < 0.001). The mean percentage of reduction in colony count for Dycal was significantly greater than that of Fuji II LC (p = 0.014), Calcimol LC (p = 0.003), and TheraCal LC (p = 0.001). ACTIVA BioACTIVE did not significantly differ from the other materials as regards antibacterial activity. Dycal showed significantly higher antibacterial activity than the other materials.
Keywords: ACTIVA BioACTIVE-BASE LINER; Dental pulp capping; Lactobacillus casei; MTT formazan; Streptococcus mutans; anti-bacterial agents.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Compressive Strength of Several Pulp Capping Materials.J Dent (Shiraz). 2021 Mar;22(1):41-47. doi: 10.30476/DENTJODS.2020.83964.1063. J Dent (Shiraz). 2021. PMID: 33681422 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of resveratrol application with pulp-capping materials on the genetic expression levels of stem cells.Int Endod J. 2020 Sep;53(9):1253-1263. doi: 10.1111/iej.13345. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Int Endod J. 2020. PMID: 32515014
-
Effect of Bioinductive Cavity Liners on Shear Bond Strength of Dental Composite to Dentin.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Mar 18;2022:3283211. doi: 10.1155/2022/3283211. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35342752 Free PMC article.
-
Bio-Inductive Materials in Direct and Indirect Pulp Capping-A Review Article.Materials (Basel). 2020 Mar 7;13(5):1204. doi: 10.3390/ma13051204. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32155997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TheraCal LC: From Biochemical and Bioactive Properties to Clinical Applications.Int J Dent. 2018 Mar 26;2018:3484653. doi: 10.1155/2018/3484653. eCollection 2018. Int J Dent. 2018. PMID: 29785184 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases