Antibiofilm and antithrombotic hydrogel coating based on superhydrophilic zwitterionic carboxymethyl chitosan for blood-contacting devices
- PMID: 38204564
- PMCID: PMC10777421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.12.009
Antibiofilm and antithrombotic hydrogel coating based on superhydrophilic zwitterionic carboxymethyl chitosan for blood-contacting devices
Abstract
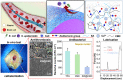
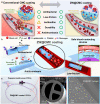
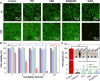
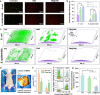
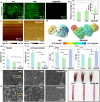
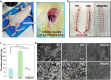
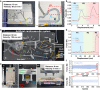
Blood-contacting devices must be designed to minimize the risk of bloodstream-associated infections, thrombosis, and intimal lesions caused by surface friction. However, achieving effective prevention of both bloodstream-associated infections and thrombosis poses a challenge due to the conflicting nature of antibacterial and antithrombotic activities, specifically regarding electrostatic interactions. This study introduced a novel biocompatible hydrogel of sodium alginate and zwitterionic carboxymethyl chitosan (ZW@CMC) with antibacterial and antithrombotic activities for use in catheters. The ZW@CMC hydrogel demonstrates a superhydrophilic surface and good hygroscopic properties, which facilitate the formation of a stable hydration layer with low friction. The zwitterionic-functionalized CMC incorporates an additional negative sulfone group and increased negative charge density in the carboxyl group. This augmentation enhances electrostatic repulsion and facilitates the formation of hydration layer. This leads to exceptional prevention of blood clotting factor adhesion and inhibition of biofilm formation. Subsequently, the ZW@CMC hydrogel exhibited biocompatibility with tests of in vitro cytotoxicity, hemolysis, and catheter friction. Furthermore, in vivo tests of antithrombotic and systemic inflammation models with catheterization indicated that ZW@CMC has significant advantages for practical applications in cardiovascular-related and sepsis treatment. This study opens a new avenue for the development of chitosan-based multifunctional hydrogel for applications in blood-contacting devices.
Keywords: Antimicrobial; Blood-clotting; Hydrogel; Sepsis; Zwitterionic.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Facile Fabrication of Multifunctional Hydrogel Nanoweb Coating Using Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Based Short Nanofibers for Blood-Contacting Medical Devices.Nano Lett. 2024 Jul 24;24(29):8920-8928. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.4c01659. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Nano Lett. 2024. PMID: 38874568
-
Dressing Blood-Contacting Materials by a Stable Hydrogel Coating with Embedded Antimicrobial Peptides for Robust Antibacterial and Antithrombus Properties.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021 Aug 25;13(33):38947-38958. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c05167. Epub 2021 Aug 16. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021. PMID: 34433245
-
High-density zwitterionic polymer brushes exhibit robust lubrication properties and high antithrombotic efficacy in blood-contacting medical devices.Acta Biomater. 2024 Apr 1;178:111-123. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.02.032. Epub 2024 Feb 27. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38423351
-
A nitric oxide-catalytically generating carboxymethyl chitosan/sodium alginate hydrogel coating mimicking endothelium function for improving the biocompatibility.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Dec 31;253(Pt 1):126727. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126727. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37673159
-
Mechanical-Enhanced and Durable Zwitterionic Hydrogel Coating for Inhibiting Coagulation and Reducing Bacterial Infection.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Aug;13(20):e2400126. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202400126. Epub 2024 May 30. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 38768441
Cited by
-
Developing fibrin-based biomaterials/scaffolds in tissue engineering.Bioact Mater. 2024 Aug 15;40:597-623. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.08.006. eCollection 2024 Oct. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 39239261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temperature-Responsive Injectable Composite Hydrogels Based on Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide), Chitosan, and Hemp-Derived Cellulose Nanocrystals.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Oct 24;16(21):2984. doi: 10.3390/polym16212984. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518194 Free PMC article.
-
Polydopamine-Cloaked Nanoarchitectonics of Prussian Blue Nanoparticles Promote Functional Recovery in Neonatal and Adult Ischemic Stroke Models.Biomater Res. 2024 Sep 18;28:0079. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0079. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39296854 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel-based cardiac patches for myocardial infarction therapy: Recent advances and challenges.Mater Today Bio. 2024 Nov 7;29:101331. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101331. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39619639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic and therapeutic strategies in combating implanted medical device-associated bacterial biofilm infections.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2025 Apr;70(2):321-342. doi: 10.1007/s12223-025-01242-y. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2025. PMID: 39865215 Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization (Who) 2021. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs)https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...
-
- Yang P.-S., Kim D., Sung J.-H., Jang E., Yu H.T., Kim T.-H., Uhm J.-S., Kim J.-Y., Pak H.-N., Lee M.-H., Joung B. Reduction of mortality by catheter ablation in real-world atrial fibrillation patients with heart failure. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:4694. doi: 10.1038/2Fs41598-021-84256-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lv Y., Huang X., Lan Y., Xia Q., Chen F., Wu J., Li W., Cao H., Xie C., Li L., Han H., Wang H., Xiang Q. Peripherally inserted central catheters have a protective role and the effect of fluctuation curve feature in the risk of bloodstream infection compared with central venous catheters: a propensity-adjusted analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022;22:289. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07265-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

