Unprecedented effect of vitamin D3 on T-cell receptor beta subunit and alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression in a 3-nitropropionic acid induced mouse model of Huntington's disease
- PMID: 38204575
- PMCID: PMC10776327
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2023.07.001
Unprecedented effect of vitamin D3 on T-cell receptor beta subunit and alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expression in a 3-nitropropionic acid induced mouse model of Huntington's disease
Abstract
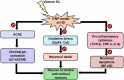
Introduction: 3-NP induction in rodent models has been shown to induce selective neurodegeneration in the striatum followed by the cortex (Brouillet, 2014). However, it remains unclear whether, under such a neurotoxic condition, characterized by neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, the gene expression of the immune resident protein, T-cell receptor beta subunit (TCR-β), α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (α7 nAChRs), the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6), and antioxidants (Cat and GpX4) get modulated on Vitamin D3 (VD) supplementation in the central nervous system.
Methods: In the present study, real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed to study the expression of respective genes. Male C57BL/6 mice (8-12 weeks) were divided into four groups namely, Group I: Control (saline); Group II: 3-NP induction via i.p (HD); Group III: Vitamin D3 (VD) and Group IV: (HD + VD) (Manjari et al., 2022).
Results: On administration of 500IU/kg/day of VD, HD mice showed a significant reduction in the gene expression of the immune receptor, TCR-β subunit, nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), inflammatory cytokines, and key antioxidants, followed by a decrease in the acetylcholinesterase activity.
Conclusion: A novel neuroprotective effect of VD in HD is demonstrated by combating the immune receptor, TCR-β gene expression, antioxidant markers, and inflammatory cytokines. In addition, HD mice on VD administration for 0-15 days showed an enhancement in cholinergic signaling with restoration in α7 nAChRs mRNA and protein expression in the striatum and cortex.
Keywords: Huntington’s disease (HD); Immune receptors; Interleukin-6 (IL-6); Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB); T-cell receptor-beta subunit (TCR- β); Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α); Vitamin D3 (VD); α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (α7 nAChRs).
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Restorative Action of Vitamin D3 on Motor Dysfunction Through Enhancement of Neurotrophins and Antioxidant Expression in the Striatum.Neuroscience. 2022 Jun 1;492:67-81. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.03.039. Epub 2022 Apr 10. Neuroscience. 2022. PMID: 35413386
-
Activation of alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by tropisetron mitigates 3-nitropropionic acid-induced Huntington's disease in rats: Role of PI3K/Akt and JAK2/NF-κB signaling pathways.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 Apr 25;393:110957. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.110957. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 38513929
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of astroglial α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are mediated by inhibition of the NF-κB pathway and activation of the Nrf2 pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Sep 26;14(1):192. doi: 10.1186/s12974-017-0967-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2017. PMID: 28950908 Free PMC article.
-
[Dual Roles of α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Expressed in Immune Cells in T Cell Differentiation -α7 nAChRs Exert Different Actions between Antigen-presenting Cells and CD4+ T Cells].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020;140(12):1421-1425. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.20-00151. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020. PMID: 33268683 Review. Japanese.
-
Role of the α7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor and RIC-3 in the Cholinergic Anti-inflammatory Pathway.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2017;17(2):90-99. doi: 10.2174/1871524916666160829114533. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27573666 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting Neuronal Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Upregulation in Age-Related Neurological Disorders.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jul 16;45(1):70. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01586-6. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40668334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tremendous Fidelity of Vitamin D3 in Age-related Neurological Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep;61(9):7211-7238. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03989-w. Epub 2024 Feb 19. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38372958 Review.
References
-
- Bakhtiari-Dovvombaygi H., Izadi S., Zare M., Asgari Hassanlouei E., Dinpanah H., Ahmadi-Soleimani S.M., Beheshti F. Vitamin D3 administration prevents memory deficit and alteration of biochemical parameters induced by unpredictable chronic mild stress in rats. Sci. Rep. 2021;11 doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-95850-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
