Comparing Opioid with Opioid-free Anesthesia Technique in Neonates Undergoing Tracheoesophageal Fistula Repair
- PMID: 38204595
- PMCID: PMC10776962
- DOI: 10.5001/omj.2023.98
Comparing Opioid with Opioid-free Anesthesia Technique in Neonates Undergoing Tracheoesophageal Fistula Repair
Abstract
Objectives: Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a congenital disorder that presents as a surgical emergency in neonates. In regions where neonatal intensive care unit facilities and resources are inadequate and skilled personnel are scarce, not extubating neonates on table, contributes to mortality. Our aim was to assess and compare the on-table extubation rate, extubation time, and postoperative pain scores between opioid and opioid-free anesthesia techniques in neonates undergoing surgical repair of TEF.
Methods: We conducted a prospective, single-blind, randomized trial over 18 months between January 2021 and June 2022 in Safdarjung Hospital, New Delhi on 60 full-term neonates scheduled for TEF surgeries randomly allocated to two groups according to the mode of analgesia administered. Group O were given fentanyl injection 1 µg/kg intravenous (IV) loading dose with IV injection. acetaminophen at 7.5 mg/kg and top-up of 0.25 µg/kg fentanyl IV si opus sit. Group NO were given pre-surgical local infiltration and intercostal block with 0.25% and 0.5% bupivacaine, respectively, with IV acetaminophen at 7.5 mg/kg.
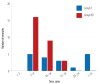
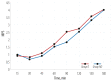
Results: Mean age in days, gender distribution, and weight in both groups were statistically comparable. The difference in the number of neonates extubated on table was statistically significant (p =0.002) in group NO compared to group O. Lower mean extubation time was seen in group NO (9.0 min 40.0 secs±3.0 min 3.0 secs) compared to group O (16.0 min 45.0 secs±8.0 min 5.0 secs) (p < 0.001). There was a statistically significant (p =0.010) lower Neonatal Infant Pain Scale score in group NO with mean and SD as 1.8±0.8 compared with group O, 2.5±1.1 at 90 min.
Conclusions: In neonates undergoing TEF repair, opioid-free anesthesia is a safe and effective method, providing a better extubation rate, faster time to extubation, and better postoperative pain control.
Keywords: Airway Extubation; Analgesics, Opioid; Fentanyl; Infant, Newborn; Tracheoesophageal Fistula.
Copyright © 2023, Oman Medical Journal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of intravenous fentanyl versus caudal epidural in neonates undergoing tracheoesophageal fistula surgeries.Saudi J Anaesth. 2022 Apr-Jun;16(2):182-187. doi: 10.4103/sja.sja_847_21. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Saudi J Anaesth. 2022. PMID: 35431742 Free PMC article.
-
On-table extubation in neonates undergoing anoplasty: an experience of anesthetic management on the concept of fast-tracking anesthesia: A pilot study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Jan;98(2):e14098. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014098. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30633221 Free PMC article.
-
The addition of tramadol to the standard of i.v. acetaminophen and morphine infusion for postoperative analgesia in neonates offers no clinical benefit: a randomized placebo-controlled trial.Paediatr Anaesth. 2014 Nov;24(11):1149-57. doi: 10.1111/pan.12477. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Paediatr Anaesth. 2014. PMID: 25040756 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of wound infiltration with bupivacaine on postoperative analgesia in neonates and infants undergoing major abdominal surgery: a pilot randomized controlled trial.J Anesth. 2012 Aug;26(4):541-4. doi: 10.1007/s00540-012-1355-0. Epub 2012 Mar 4. J Anesth. 2012. PMID: 22391668 Clinical Trial.
-
Subtenon block compared to intravenous fentanyl for perioperative analgesia in pediatric cataract surgery.Anesth Analg. 2009 Apr;108(4):1132-8. doi: 10.1213/ane.0b013e318198a3fd. Anesth Analg. 2009. PMID: 19299775 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Al-Rawi O, Booker PD. Oesophageal atresia and tracheo-oesophageal fistula. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain 2007;7(1):15-19 .10.1093/bjaceaccp/mkl062 - DOI
-
- Morton NS, Fairgrieve R, Moores A, Wallace E. Anesthesia for the full-term and ex-premature infant. Gregory’s Pediatric Anesthesia 2020:533.
-
- Charki S, Priyadarashini M, Hadalgi L, Agarwal S, Kulkarni T, Loni R, et al. . Experience of tracheo-esophageal fistula in neonates in a tertiary care center - case series. J Clin Neonatol 2019;8(2):71 .10.4103/jcn.JCN_69_18 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources