Flavonoids and fibrate modulate apoE4-induced processing of amyloid precursor protein in neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 38204816
- PMCID: PMC10777729
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1245895
Flavonoids and fibrate modulate apoE4-induced processing of amyloid precursor protein in neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
Introduction: Apolipoprotein (apo) E4, being a major genetic risk factor for Alzheimer's disease (AD), is actively involved in the proteolytic processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) to amyloid β (Aβ) peptide, the principle constituent of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer Disease (AD) patients. ApoE4 is believed to affect APP processing through intracellular cholesterol homeostasis, whereas lowering the cholesterol level by pharmacological agents has been suggested to reduce Aβ production. This study has investigated the effects of hypolipidemic agents fenofibrate, and the flavonoids-naringenin and diosmetin-on apoE4-induced APP processing in rat neuroblastoma cells stably transfected with human wild-type APP 695 (B103-hAPP695wt).
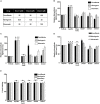
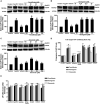
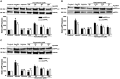
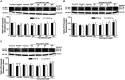
Results: B103-hAPP695wt cells were pretreated with different doses of flavonoids and fenofibrate for 1 h prior to apoE4 exposure for 24 h. ApoE4-induced production of intra- and extracellular Aβ peptides has been reduced with fenofibrate, naringenin, and diosmetin treatments. Pretreatment with diosmetin has significantly reduced apoE4-induced full-length APP (fl- APP) expression, whereas naringenin and fenofibrate had no effect on it. In addition, the increase in the apoE4-induced secretion of sAPPtotal and sAPPα has been dose-dependently reduced with drug pretreatment. On the other hand, the decrease in the expression of both APP-carboxy terminal fragments (CTF)-α and -β (generated by the α- or β-secretase cleavage of APP) by apoE4 was dose-dependently increased in cells pretreated with fenofibrate and naringenin but not diosmetin.
Conclusion: Thus, we suggest that fenofibrate, naringenin, and diosmetin treatments can reduce apoE4- induced Aβ production by distinct mechanisms that may prove useful in developing drugs for AD patients.
Keywords: APP; amyloid β; apoE4; diosmetin; fibrates; flavonoids; naringenin; neuronal cells.
Copyright © 2023 Davra and Benzeroual.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein (apo) E4 enhances amyloid beta peptide production in cultured neuronal cells: apoE structure as a potential therapeutic target.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Dec 20;102(51):18700-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0508693102. Epub 2005 Dec 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16344478 Free PMC article.
-
Abca1 deficiency affects Alzheimer's disease-like phenotype in human ApoE4 but not in ApoE3-targeted replacement mice.J Neurosci. 2012 Sep 19;32(38):13125-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1937-12.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22993429 Free PMC article.
-
Specific antibody binding to the APP672-699 region shifts APP processing from α- to β-cleavage.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Aug 14;5(8):e1374. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.336. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25118934 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Alzheimer's disease in transgenic mice: effect of age and of presenilin1 on amyloid biochemistry and pathology in APP/London mice.Exp Gerontol. 2000 Sep;35(6-7):831-41. doi: 10.1016/s0531-5565(00)00149-2. Exp Gerontol. 2000. PMID: 11053674 Review.
-
Advances in the cellular and molecular biology of the beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease.Neuromolecular Med. 2002;1(1):1-31. doi: 10.1385/NMM:1:1:1. Neuromolecular Med. 2002. PMID: 12025813 Review.
Cited by
-
Detergent-free isolation and characterization of amyloid precursor protein C99 in E. coli native lipid-nanodiscs using non-ionic polymer.Protein Sci. 2025 Sep;34(9):e70276. doi: 10.1002/pro.70276. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 40828514 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Flavonoids in Protecting Against Neurodegenerative Diseases-Possible Mechanisms of Action.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 16;26(10):4763. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104763. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429904 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Assaf N., El-Shamarka M. E., Salem N. A., Khadrawy Y. A., El Sayed N. S. (2020). Neuroprotective effect of PPAR alpha and gamma agonists in a mouse model of amyloidogenesis through modulation of the Wnt/beta catenin pathway via targeting alpha- and beta-secretases. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 97:109793. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2019.109793 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

