Effects of 12-Week Combined Strength and Endurance Circuit Training Program on Insulin Sensitivity and Retinol-Binding Protein 4 in Women with Insulin-Resistance and Overweight or Mild Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 38204866
- PMCID: PMC10778163
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S432954
Effects of 12-Week Combined Strength and Endurance Circuit Training Program on Insulin Sensitivity and Retinol-Binding Protein 4 in Women with Insulin-Resistance and Overweight or Mild Obesity: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Circuit training is an exercise mode, that may include both endurance and resistance components. There are premises that a combination of these two modalities brings additional benefits, particularly in improving insulin sensitivity. The retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) may inhibit signaling from insulin metabolic pathways in skeletal muscles, thus developing insulin resistance. This study aimed to evaluate whether moderate intensity circuit training combining strength and endurance exercise induces changes in tissue insulin sensitivity, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, and serum RBP4 levels in insulin-resistant women.
Methods: In this clinical controlled trial women diagnosed with insulin-resistance were randomly divided into two groups. The training group (T) performed circuit training combining strength (50%-80%1RM) and endurance (50%-75%HRR) exercise on five weight and two cardio machines, for 33 minutes, three times per week, for 3 months. Women from the control non-training group (NT) did not change their previous physical activity. At the beginning of the study and after the intervention period, a one-repetition maximum, body mass, and composition, resting heart rate (HR), blood pressure, glucose, insulin, blood lipids, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), RBP4, and insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) were measured. The results of 27 patients were analyzed using a two-way repeated measures ANOVA.
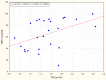
Results: Significant differences in the pattern of change over time between the groups for resting HR (p < 0.010) and total lean mass (p < 0.039) were found. No differences in HOMA-IR, and RBP4 were observed post-study compared to pre-study in the T group. A significant correlation between RBP4 and TSH concentration was found.
Conclusion: Twelve-week circuit training combining strength and endurance exercise has minor effects on HOMA-IR, glucose and lipid metabolism, IGF-1, TSH, and RBP4. Although moderate-intensity circuit training is considered safe, its effectiveness in patients with overweight and mild obesity may be insufficient to reduce insulin resistance.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04528693, registered August 23, 2020.
Keywords: exercise program; insulin resistance; insulin-like growth factors-1; retinol-binding protein 4; thyroid-stimulating hormone.
© 2024 Ratajczak et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of a Circuit Training Program on Myokine Levels in Insulin-Resistant Women: A Randomised Controlled Trial.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Nov 28;2024:6624919. doi: 10.1155/jdr/6624919. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 39640300 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Impact of Exercise Training Intensity on Physiological Adaptations and Insulin Resistance in Women with Abdominal Obesity.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;10(12):2533. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10122533. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36554057 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and prevalence of nonresponders after 12 weeks of high-intensity interval or resistance training in women with insulin resistance: a randomized trial.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017 Apr 1;122(4):985-996. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01037.2016. Epub 2017 Feb 2. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017. PMID: 28153946 Clinical Trial.
-
Changes of serum retinol-binding protein 4 associated with improved insulin resistance after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy in Chinese obese patients.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2020 Jan 14;12:7. doi: 10.1186/s13098-019-0511-1. eCollection 2020. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2020. PMID: 31956345 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise in weight management of obesity.Cardiol Clin. 2001 Aug;19(3):459-70. doi: 10.1016/s0733-8651(05)70229-0. Cardiol Clin. 2001. PMID: 11570117 Review.
Cited by
-
Retinol binding protein 4 and type 2 diabetes: from insulin resistance to pancreatic β-cell function.Endocrine. 2024 Sep;85(3):1020-1034. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-03777-5. Epub 2024 Mar 23. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 38520616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of dietary and circulating antioxidant vitamins with metabolic syndrome: an observational and Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 14;15:1446719. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1446719. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39469581 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of low-intensity resistance training at different levels of blood flow restriction on pain, proprioception and muscle strength in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Aug 8;26(1):769. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-09051-7. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40781308 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a Circuit Training Program on Myokine Levels in Insulin-Resistant Women: A Randomised Controlled Trial.J Diabetes Res. 2024 Nov 28;2024:6624919. doi: 10.1155/jdr/6624919. eCollection 2024. J Diabetes Res. 2024. PMID: 39640300 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Vargas E, Podder V, Carrillo Sepulveda MA. Physiology, glucose transporter type 4. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2022, StatPearls Publishing LLC.; 2022. - PubMed
Publication types
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous