Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of antisense peptide nucleic acids
- PMID: 38204913
- PMCID: PMC10777018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.102086
Therapeutic and diagnostic applications of antisense peptide nucleic acids
Abstract
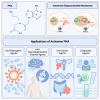
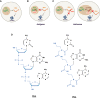
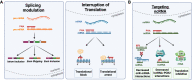
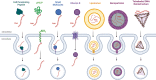
Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) are synthetic nucleic acid analogs with a neutral N-(2-aminoethyl) glycine backbone. PNAs possess unique physicochemical characteristics such as increased resistance to enzymatic degradation, ionic strength and stability over a wide range of temperatures and pH, and low intrinsic electrostatic repulsion against complementary target oligonucleotides. PNA has been widely used as an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO). Despite the favorable characteristics of PNA, in comparison with other ASO technologies, the use of antisense PNA for novel therapeutics has lagged. This review provides a brief overview of PNA, its antisense mechanisms of action, delivery strategies, and highlights successful applications of PNA, focusing on anti-pathogenic, anti-neurodegenerative disease, anti-cancer, and diagnostic agents. For each application, several studies are discussed focusing on the different target sites of the PNA, design of different PNAs and the therapeutic outcome in different cell lines and animal models. Thereafter, persisting limitations slowing the successful integration of antisense PNA therapeutics are discussed in order to highlight actionable next steps in the development and optimization of PNA as an ASO.
Keywords: ASO; MT: Oligonucleotides; Nucleic acid Therapies and Applications; PNA; antisense; miRNA; oligonucleotide; peptide nucleic acids.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential of Peptide Nucleic Acids in Future Therapeutic Applications.Adv Pharm Bull. 2018 Nov;8(4):551-563. doi: 10.15171/apb.2018.064. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Adv Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 30607328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptide-nucleic acids (PNAs): a tool for the development of gene expression modifiers.Curr Pharm Des. 2001 Nov;7(17):1839-62. doi: 10.2174/1381612013397087. Curr Pharm Des. 2001. PMID: 11562312 Review.
-
Peptide nucleic acids: Advanced tools for biomedical applications.J Biotechnol. 2017 Oct 10;259:148-159. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.07.026. Epub 2017 Jul 29. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28764969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A highly effective and long-lasting inhibition of miRNAs with PNA-based antisense oligonucleotides.Mol Cells. 2009 Oct 31;28(4):341-5. doi: 10.1007/s10059-009-0134-8. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Mol Cells. 2009. PMID: 19812898
-
Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) antisense effect to bacterial growth and their application potentiality in biotechnology.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 Mar;86(2):397-402. doi: 10.1007/s00253-009-2387-8. Epub 2010 Feb 5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20135118 Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Modulation with Oral DNA/RNA Nanoparticles.Pharmaceutics. 2025 May 4;17(5):609. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17050609. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40430900 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fmoc Solid-Phase FIT-PNA Synthesis-Manual and Automated Methodologies.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2934:189-207. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4578-9_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40663332
-
Current perspectives in drug targeting intrinsically disordered proteins and biomolecular condensates.BMC Biol. 2025 May 6;23(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02214-x. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40325419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Cutting-Edge Technologies for the Delivery of Peptide Nucleic Acid.Chemistry. 2025 Jun 17;31(34):e202500469. doi: 10.1002/chem.202500469. Epub 2025 May 21. Chemistry. 2025. PMID: 40351137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Facile Synthesis of Red-Shifted Bis-Quinoline (BisQ) Surrogate Base.Molecules. 2024 Aug 31;29(17):4136. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174136. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39274984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller P.S. In: Cohn W.E., Moldave K., editors. Vol. 52. Academic Press; 1996. Development of Antisense and Antigene Oligonucleotide Analogs; pp. 261–291. (Progress in Nucleic Acid Research and Molecular Biology). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

