Salivary biomarkers for early detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and head/neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 38204964
- PMCID: PMC10776379
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdsr.2023.10.003
Salivary biomarkers for early detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and head/neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
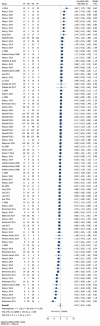
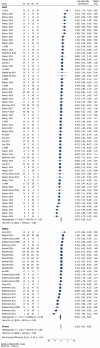
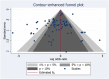
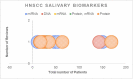
Oral cancer became a very common condition. WHO estimates that there are 4 cases of lip and oral cavity cancer for every 100,000 people worldwide. The early diagnosis of cancers is currently a top focus in the health sector. Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have identified promising biomarkers for early detection in several original research investigations. However, it is still unclear the quality of these evidence and which biomarker performs the best in terms of early detection. Therefore, the objective was, to map the methodological and reporting quality of available oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) or head/neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) systematic reviews and meta-analysis. Secondly, to evaluate diagnostic accuracy of salivary biomarkers for common craniofacial cancers and to compare the diagnostic value of different salivary biomarkers. PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase and Cochrane Library electronic databases were used to map the methodological and reporting quality of the systematic reviews and meta-analysis conducted on the HNSCC, OSCC using the AMSTAR-2 checklist. The inclusion criteria were systematic reviews and meta-analysis published in the topic of HNSCC and OSCC biomarkers. Exclusion criteria were no animal studies; original primary studies, due to limitation of competency in other languages articles with language other than English were excluded. The sensitivity and specificity were calculated for salivary biomarkers and ranked according to network meta-analysis principles. A total of N = 5893 patients were included from four meta-analysis studies. All together, these included n = 37 primary studies. n = 94 biomarkers were pooled from these four meta-analyses and categorised into the stages at which they were detected (I-IV). In OSCC, Chemerin and MMP-9 displayed the highest sensitivity, registering 0.94 (95% CI 0.78, 1.00) and a balanced accuracy of 0.93. Phytosphingosine closely followed, with a sensitivity of 0.91 (95% CI 0.68, 0.99) and a balanced accuracy of 0.87. For HNSCC, the top three biomarkers are Actin, IL-1β Singleplex, and IL-8 ELISA. Actin leads with a sensitivity of 0.91 (95% CI 0.68-0.99), a specificity of 0.67, and an overall accuracy of 0.79. Subsequently, IL-1β Singleplex exhibits a sensitivity of 0.62 (95% CI 0.30-0.88), a specificity of 0.89, and an accuracy of 0.75, followed by IL-8 ELISA with a sensitivity of 0.81 (95% CI 0.54-0.97), a specificity of 0.59, and an accuracy of 0.70. In conclusion, there was highest sensitivity for MMP-9 and chemerin salivary biomarkers. There is need of further more studies to identify biomarkers for HNSCC and OSCC.
Keywords: Biological; Biomarker; Cancers; HNSCC; Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Marker; Mouth; NMA; Network meta-analysis; OSCC; Oral cancer; Oral neoplasm; Saliva.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures



References
-
- Dillon M., Smith D.J., Kanatas A. Oral cancer: another challenge for the dental team? Br Dent J. 2016;220:499–500. - PubMed
-
- Global Health Data Exchange | GHDx Available online: 〈http://ghdx.healthdata.org/〉 (accessed on 4 February 2022).
-
- Khalili J. Oral cancer and role of general dental practitioners in its early detection. Lik Sprav. 2007:10–19. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

