Role of Arctiin in Fibrosis and Apoptosis in Experimentally Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Rats
- PMID: 38205087
- PMCID: PMC10777261
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.51997
Role of Arctiin in Fibrosis and Apoptosis in Experimentally Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Rats
Abstract
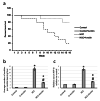
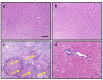
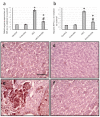
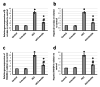
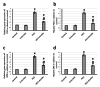
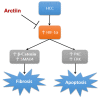
Background and objectives Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly aggressive malignant tumor with a poor prognosis. It is currently the second most common cause of cancer-related mortality. Arctiin, a compound found in plants commonly used as a vegetable in Asian countries and as an ingredient in traditional European dishes, possesses various properties, including anti-proliferative, anti-senescence, anti-oxidative, anti-tumor, toxic, anti-adipogenic, and anti-bacterial effects. Our study aims to investigate the potential antitumor activity of arctiin against HCC in rats by inhibiting cell fibrosis and apoptosis. Methods Rats were induced with HCC by administering thioacetamide. Arctiin was orally administered to some rats twice a week for 16 weeks at a dose of 30 mg/kg. The liver impairment was evaluated by measuring serum α-fetoprotein (AFP) and examining liver sections stained with Masson trichrome or anti-hypoxia-induced factor-1α (HIF-1α) antibodies. The hepatic expression of messenger RNA and protein levels of HIF-1α, protein kinase C (PKC), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), β-catenin, and mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 (SMAD4) were analyzed. Results Our study demonstrated that arctiin can potentially increase the survival rate of rats. This is achieved through a reduction in serum AFP levels and hepatic nodules. We also observed that arctiin has the ability to inhibit the formation of fibrotic tissues and necrotic nodules in HCC rats. Additionally, arctiin can significantly decrease the expression of HIF-1α, PKC, ERK, β-catenin, and SMAD4. Conclusion Arctiin has demonstrated potential anti-tumor properties that could ameliorate HCC. Studies have shown that it may increase survival rates and reduce the number of tumors and AFP levels. Arctiin works by inhibiting HCC-induced hypoxia, thus blocking the expression of HIF-1α. It also helps to slow down tumor fibrosis by decreasing the expression of β-catenin and SMAD4. Furthermore, arctiin has been found to downregulate PKC and ERK, reducing hepatic tissue apoptosis.
Keywords: extracellular signal-regulated kinase (erk); hepatocellular carcinoma (hcc); hypoxia-induced factor-1α (hif-1α); mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 (smad4); protein kinase c (pkc); β-catenin.
Copyright © 2024, Alshehri et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ferulic acid inhibits tumor proliferation and attenuates inflammation of hepatic tissues in experimentally induced HCC in rats.J Investig Med. 2024 Dec;72(8):900-910. doi: 10.1177/10815589241270489. Epub 2024 Aug 14. J Investig Med. 2024. PMID: 39091053
-
Echinacoside ameliorates hepatic fibrosis and tumor invasion in rats with thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Sep 6;24(5):1186-1198. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10367. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38461536 Free PMC article.
-
Physical exercise suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression by alleviating hypoxia and attenuating cancer stemness through the Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway.J Integr Med. 2023 Mar;21(2):184-193. doi: 10.1016/j.joim.2023.01.002. Epub 2023 Jan 20. J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 36781361
-
Pleiotropic effects of methionine adenosyltransferases deregulation as determinants of liver cancer progression and prognosis.J Hepatol. 2013 Oct;59(4):830-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.04.031. Epub 2013 May 7. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23665184 Review.
-
Association of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression with susceptibility to hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis.Int J Biol Markers. 2023 Dec;38(3-4):149-158. doi: 10.1177/03936155231204391. Epub 2023 Oct 3. Int J Biol Markers. 2023. PMID: 37787154 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of modulating the extracellular matrix cross linkage by genipin on tumor cell resistance and survival in thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats.PeerJ. 2025 Jul 9;13:e19680. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19680. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40656954 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Genetic Screening on the Syndromes of Colorectal Cancer and Gastric Cancer: A 2024 Update.Biomedicines. 2024 Nov 21;12(12):2655. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122655. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating anticancer activity of emodin by enhancing antioxidant activities and affecting PKC/ADAMTS4 pathway in thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rats.Redox Rep. 2024 Dec;29(1):2365590. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2024.2365590. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Redox Rep. 2024. PMID: 38861483 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Effects of Arctiin on Alzheimer's Disease-like Model in Rats by Reducing Oxidative Stress, Inflammasomes and Fibrosis.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024;21(4):276-288. doi: 10.2174/0115672050333388240801043509. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024. PMID: 39136502
-
Effects of Cycloastragenol on Alzheimer's Disease in Rats by Reducing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024;21(2):141-154. doi: 10.2174/0115672050315334240508162754. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2024. PMID: 38766828
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
