Pathways of Media Contact to Health Literacy in Middle-Aged and Older People: The Chain Mediation Effect of Perceived Social Support and Self-Efficacy
- PMID: 38205129
- PMCID: PMC10778256
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S448223
Pathways of Media Contact to Health Literacy in Middle-Aged and Older People: The Chain Mediation Effect of Perceived Social Support and Self-Efficacy
Abstract
Objective: To understand the status of media exposure, social support, self-efficacy, and health literacy among middle-aged and older adults in China, and explore the impact path of media exposure on the health literacy of this population, providing a reference for promoting their physical and mental health.
Methods: From July to November 2022, a multi-stage random sampling method was employed to survey 16,938 Chinese middle-aged and older adults aged 46 and above. Structural equation modeling and statistical analysis were conducted using LISREL 8.8 and Mplus 8.3 software.
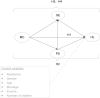
Results: The average score for media exposure among Chinese middle-aged and older adults was (18.55±5.36), perceived social support was (60.68±12.51), self-efficacy was (28.76±5.40), and health literacy was (35.49±6.05). Statistical results revealed that media exposure has a positive impact on the health literacy of middle-aged and older adults, with a direct effect of 0.091 (p < 0.001). Mediation analysis showed that media exposure can affect the health literacy of this population through the independent mediating effects of perceived social support (β = 0.013, p < 0.001) and self-efficacy (β = 0.029, p < 0.001), as well as through a chain mediation effect involving perceived social support and self-efficacy (β = 0.015, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: As a pathway for health information dissemination, media exposure plays a crucial role in the intervention of health literacy among middle-aged and older adults. Perceived social support and self-efficacy not only have independent mediating effects but also significant chain mediating effects in the relationship between media exposure and health literacy among this population. Therefore, improving the health literacy of middle-aged and older people can be popularized through media and improved in a multi-path, all-round, and precise way with the help of related technologies and social forces from which media literacy can be improved.
Keywords: health literacy; media contact; middle-aged and elderly people; self-efficacy; social support.
© 2024 Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Aging: overview. World Health Organization. Available from: https://www.who.int/health-topics/ageing#tab=tab_1. Accessed April 24, 2022.
-
- Ghorbanian M, Huvila I, Nikou S. Health Literacy, health literacy interventions and decision-making: a systematic literature review. J Doc. 2022;78(7):405–428. doi:10.1108/jd-01-2022-0004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials