Persistent Nocardia beijingensis infection in a patient with postoperative abscess and misuse of antibiotics in China
- PMID: 38205174
- PMCID: PMC10774666
- DOI: 10.1016/j.imj.2023.11.002
Persistent Nocardia beijingensis infection in a patient with postoperative abscess and misuse of antibiotics in China
Abstract
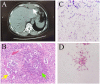
Here we describe the first case of abscess infection caused by Nocardia beijingensis in China. The patient was immunocompetent but suffered from postoperative abscess for 6 years. This study highlights the necessity of long-term infected foci to be thoroughly examined to identify the pathogen, as well as the importance of accurate Nocardia identification and antimicrobial susceptibility tests for understanding the pathogen's epidemiology, clinical significance, and treatment strategy.
Keywords: Abscess; Immunocompetent; Infection; Nocardia beijingensis.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of Tsinghua University Press.
Figures


References
-
- COMMISSION E C O R D U O T N H . third ed. People’s Health Publishing House; Beijing: 2023. National Guidelines for Antimicrobial Therapy [M] pp. 85–96.
-
- Wang L., Zhang Y., Lu Z., et al. Nocardia beijingensis sp. nov., a novel isolate from soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2001;51(Pt 5):1783–1788. - PubMed
-
- Kageyama A., Poonwan N., Yazawa K., et al. Nocardia beijingensis, is a pathogenic bacterium to humans: the first infectious cases in Thailand and Japan. Mycopathologia. 2004;157(2):155–161. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

