Efficacy of alectinib in lung adenocarcinoma patients with different anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements and co-existing alterations-a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 38205204
- PMCID: PMC10775000
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-23-658
Efficacy of alectinib in lung adenocarcinoma patients with different anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) rearrangements and co-existing alterations-a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Alectinib significantly improves survival of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearrangement. In this study, we analyzed the effects of different ALK rearrangements and co-mutations on the efficacy of alectinib.
Methods: Using the electronic medical record system, we reviewed in terms of clinical and pathological features patients with advanced (IIIB/IV stage) ALK-rearranged NSCLC at Shanghai Chest Hospital between January 2018 and December 2021 who were treated with alectinib in first or second line and were assessed for objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), and progression-free survival (PFS).
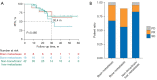
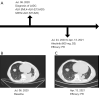
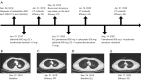
Results: A total of 66 patients were enrolled in the study, and 17 types of ALK rearrangements were detected, of which five types of ALK rearrangements responded well to alectinib. We classified ALK-rearrangements into four main types, namely echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 (EML4)-ALK (E6:A20), EML4-ALK (E13:A20), EML4-ALK (E20:A20), and others. There was no significant difference in ORR and DCR of these types (ORR: 31.3% vs. 13.0% vs. 18.2% vs. 17.6%, P=0.575; DCR: 93.8% vs. 95.6% vs. 100.0% vs. 88.2%, P=0.627). The 3-year PFS rates were 25.0% (4/16) vs. 13.0% (3/23) vs. 27.3% (3/11) vs. 18.8% (3/16) for EML4-ALK (E6:A20), EML4-ALK (E13:A20), EML4-ALK (E20:A20), and others, respectively (P=0.725). The results of co-mutation analysis showed that the median PFS (mPFS) for patients with tumors harboring TP53 mutations was 30.4 months, significantly shorter than that of patients with tumors without co-mutations and whose mPFS was not mature (P=0.026). TSC1 co-mutation was also identified as a detrimental factor in outcome, with a DCR of 60% vs. 100% (P=0.031), mPFS of 30.4 months vs. not applicable (P=0.160) in patients with vs. those without this co-mutation, respectively. The efficacy of alectinib in patients with brain metastases is comparable to that in patients without distant organ metastases. There were two cases with specific fusion types that also responded to alectinib; namely, double ALK-rearrangements: EML4-ALK (E13:A20) and MSH2-ALK (M7:A20), and with a rare fusion partner, SPECC1L-ALK (S8:A20). Their PFS were 8.7 and 38.0 months, respectively.
Conclusions: In this study, the efficacy of alectinib in different types of ALK-rearrangements varied slightly. TP53 and TSC1 co-mutations were identified as detrimental factors affecting efficacy. This study provides references for the response to alectinib in patients with different types of ALK rearrangements and co-mutation.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); alectinib; anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK); chromosomal rearrangements; co-mutated genes.
2023 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-23-658/coif). Y.Z. and X.Z. are from 3D Medicines Inc., Shanghai, China. A.R. has received advisory board honoraria from AstraZeneca, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, BMS, and Amgen; writing engagement honoraria from AstraZeneca, MSD, Roche and Novartis; speaker bureau from AstraZeneca and BMS. A.R. reports research funding from EMQN, GECP; consulting fees from AstraZeneca; payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speaker bureaus from Thermofisher Scientific, Illumina, Health in code; and travel expenses from Thermofisher Scientific, Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation, Takeda. She also serves as advisory board member in Takeda. E.M.U. reports honoraria for lectures from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Novartis; support from AstraZeneca for participation at IASLC WCLC 2023, Singapore, and advisory board member in Pfizer, Roche, Takeda. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lung adenocarcinoma harboring complex EML4-ALK fusion and BRAF V600E co-mutation responded to alectinib.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Oct 7;101(40):e30913. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030913. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36221356 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of EML4-ALK fusion variants and clinical outcomes in patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2020 Nov;149:154-161. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2020.09.012. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Lung Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33017727
-
Coexistence of a novel SV2B-ALK, EML4-ALK double-fusion in a lung poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma patient and response to alectinib: a case report and literature review.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 13;14:1453259. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1453259. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39735595 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of clinical outcomes for anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer in Chinese patients: A retrospective study.Cancer Genet. 2023 Jan;270-271:32-38. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2022.11.005. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Cancer Genet. 2023. PMID: 36502690 Review.
-
Coexistence of a novel NBEA-ALK, EML4-ALK double-fusion in a lung adenocarcinoma patient and response to alectinib: A case report.Lung Cancer. 2021 Dec;162:86-89. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2021.10.015. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34763158 Review.
Cited by
-
Refining Criteria for Choosing the First-Line Treatment for Real-World Patients with Advanced ALK-Rearranged NSCLC.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 21;26(13):5969. doi: 10.3390/ijms26135969. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-accuracy prediction of mutations in nine genes in lung adenocarcinoma via two-stage multi-instance learning on large-scale whole-slide images.Diagn Pathol. 2025 Jun 2;20(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s13000-025-01663-w. Diagn Pathol. 2025. PMID: 40457363 Free PMC article.
-
ALK-tyrosine kinase inhibitor intrinsic resistance due to de novo MET-amplification in metastatic ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer effectively treated by alectinib-crizotinib combination-case report.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):2453-2462. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-439. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39430327 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
