eIF4A dependency: the hidden key to unlock KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer's vulnerability
- PMID: 38205207
- PMCID: PMC10775007
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-23-682
eIF4A dependency: the hidden key to unlock KRAS mutant non-small cell lung cancer's vulnerability
Keywords: KRAS; MYC; Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); eukaryotic initiation factor-4A (eiF4A).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-23-682/coif). S.C.S. reports that she received support from Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness [Proyectos de I+D+i en Líneas Estratégicas” (PLEC2021- 007959) grant]; she is the author of patents directly or indirectly connected to lung cancer treatment (EP20710558, EP22383031, EP23382345 and EP23382552); she is an employee and shareholder of Peptomyc S.L., a company that develops therapeutics for cancer treatment. I.G.L. reports that he received support from BBVA Foundation [2nd Comprehensive Program of Cancer Immunotherapy & Immunology (CAIMI-II) grant] and Spanish Ministry of Universities [Grant from the University Teacher Training Program FPU (FPU20/04812)] and he is the author of one patent connected to lung cancer treatment (EP23382552). L.S. reports that she received support from Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness [Proyectos de I+D+i en Líneas Estratégicas” (PLEC2021- 007959) grant], La Marató TV3 [grant (2019429)] and BBVA Foundation [2nd Comprehensive Program of Cancer Immunotherapy & Immunology (CAIMI-II) grant]; she is the CEO and shareholder of Peptomyc S.L., a company that develops therapeutics for cancer treatment, and received consulting fees from it; she is author of patents directly or indirectly connected to lung cancer treatment (EP13382167, EP16382339, EP19382195, EP19382194, EP22383031, EP22383028, EP23382345, EP23382552, EP23382553 and EP2338255). The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
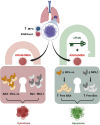
Comment on
-
Cotargeting a MYC/eIF4A-survival axis improves the efficacy of KRAS inhibitors in lung cancer.J Clin Invest. 2023 Aug 15;133(16):e167651. doi: 10.1172/JCI167651. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37384411 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of mutant KRAS-driven overexpression of ARF6 and MYC by an eIF4A inhibitor drug improves the effects of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 May 17;19(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12964-021-00733-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 34001163 Free PMC article.
-
Cotargeting a MYC/eIF4A-survival axis improves the efficacy of KRAS inhibitors in lung cancer.J Clin Invest. 2023 Aug 15;133(16):e167651. doi: 10.1172/JCI167651. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37384411 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of BET bromodomain inhibition in Kras-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 15;19(22):6183-92. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3904. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24045185 Free PMC article.
-
Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting eIF4A in Leukemia.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021;22(7):559-566. doi: 10.2174/1389203722666210526155808. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021. PMID: 34042032 Review.
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A (eIF4A) during viral infections.Virus Genes. 2019 Jun;55(3):267-273. doi: 10.1007/s11262-019-01641-7. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Virus Genes. 2019. PMID: 30796742 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploiting Translation Machinery for Cancer Therapy: Translation Factors as Promising Targets.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 9;25(19):10835. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910835. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39409166 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dempke WC. Targeted Therapy for NSCLC--A Double-edged Sword? Anticancer Res 2015;35:2503-12. - PubMed
-
- Chmielewska I, Krawczyk P, Grenda A, et al. Breaking the 'Undruggable' Barrier: Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 Immunotherapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with KRAS Mutations-A Comprehensive Review and Description of Single Site Experience. Cancers (Basel) 2023;15:3732. 10.3390/cancers15143732 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
