Exosomal ITGB6 from dormant lung adenocarcinoma cells activates cancer-associated fibroblasts by KLF10 positive feedback loop and the TGF-β pathway
- PMID: 38205211
- PMCID: PMC10775012
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-23-707
Exosomal ITGB6 from dormant lung adenocarcinoma cells activates cancer-associated fibroblasts by KLF10 positive feedback loop and the TGF-β pathway
Abstract
Background: Dormant cancer cells are commonly known to play a pivotal role in cancer recurrence and metastasis. However, the mechanism of tumor dormancy and recurrence remains largely unknown. This study aimed to investigate the mechanism by which exosomes derived from dormant lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) cells activate cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) to reconstruct the extracellular matrix (ECM), providing a novel idea for decoding the mechanism of tumor dormancy.
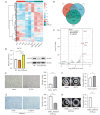
Methods: In this study, high-dose cisplatin was used to induce the dormant LUAD cells. Exosomes were extracted from the culture supernatant of normal and dormant cancer cells. The effects of selected exosomal proteins on the fibroblasts were evaluated. RNA-seq for fibroblasts and exosomal proteomics for normal and dormant cancer cells were used to identify and verify the mechanism of activating fibroblasts.
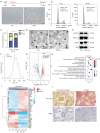
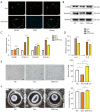
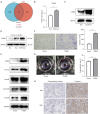
Results: We demonstrated that exosomes derived from dormant A549 cells could be taken by fibroblasts. Exosomal ITGB6 transferred into fibroblasts induced the activation of CAFs by activating the KLF10 positive feedback loop and transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) pathway. High ITGB6 expression was associated with activation of the TGF-β pathway and ECM remodeling.
Conclusions: In all, we demonstrated that CAFs were activated by exosomes from dormant lung cancer cells and reconstruct ECM. ITGB6 may be a critical molecule for activating the TGF-β pathway and remodeling ECM.
Keywords: Lung cancer; cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs); dormancy; exosomes.
2023 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-23-707/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived exosomal miR-17-5p promotes colorectal cancer aggressive phenotype by initiating a RUNX3/MYC/TGF-β1 positive feedback loop.Cancer Lett. 2020 Oct 28;491:22-35. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.07.023. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32730779
-
Exo-miR-1290-induced by COX-2 overexpression promotes cancer-associated fibroblasts activation and tumor progression by CUL3-Nrf2 pathway in lung adenocarcinoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Sep 18;21(1):242. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01268-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37723559 Free PMC article.
-
Colorectal cancer cell-derived exosomes containing miR-10b regulate fibroblast cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway.Bull Cancer. 2018 Apr;105(4):336-349. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2017.12.009. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Bull Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29496262
-
Exosomal miRNAs and miRNA dysregulation in cancer-associated fibroblasts.Mol Cancer. 2017 Aug 29;16(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0718-4. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28851377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of heterogeneous cancer-associated fibroblasts: the molecular pathology of activated signaling pathways.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 16;39(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01611-0. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32546182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomal Proteomics: Unveiling Novel Insights into Lung Cancer.Aging Dis. 2024 Apr 9;16(2):876-900. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0409. Aging Dis. 2024. PMID: 38607736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Navigating the Complexity of Resistance in Lung Cancer Therapy: Mechanisms, Organoid Models, and Strategies for Overcoming Treatment Failure.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Nov 28;16(23):3996. doi: 10.3390/cancers16233996. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asthma-derived genetic signature predicts lung cancer prognosis: a multi-scale omics investigation.J Thorac Dis. 2025 Mar 31;17(3):1400-1423. doi: 10.21037/jtd-24-1697. Epub 2025 Mar 26. J Thorac Dis. 2025. PMID: 40223964 Free PMC article.
-
Role of exosomes in transforming growth factor-β-mediated cancer cell plasticity and drug resistance.Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025 Jun 5;6:1002322. doi: 10.37349/etat.2025.1002322. eCollection 2025. Explor Target Antitumor Ther. 2025. PMID: 40486962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes in inflammation and cancer: from bench to bedside applications.Mol Biomed. 2025 Jun 10;6(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s43556-025-00280-9. Mol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 40490663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
