YTHDF3 modulates the Cbln1 level by recruiting BTG2 and is implicated in the impaired cognition of prenatal hypoxia offspring
- PMID: 38205248
- PMCID: PMC10776956
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108703
YTHDF3 modulates the Cbln1 level by recruiting BTG2 and is implicated in the impaired cognition of prenatal hypoxia offspring
Abstract
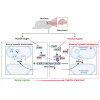
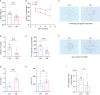
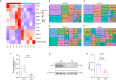
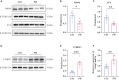
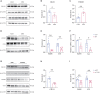
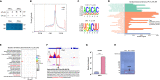
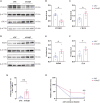
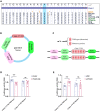
The "Fetal Origins of Adult Disease (FOAD)" hypothesis holds that adverse factors during pregnancy can increase the risk of chronic diseases in offspring. Here, we investigated the effects of prenatal hypoxia (PH) on brain structure and function in adult offspring and explored the role of the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) pathway. The results suggest that abnormal cognition in PH offspring may be related to the dysregulation of the m6A pathway, specifically increased levels of YTHDF3 in the hippocampus. YTHDF3 interacts with BTG2 and is involved in the decay of Cbln1 mRNA, leading to the down-regulation of Cbln1 expression. Deficiency of Cbln1 may contribute to abnormal synaptic function, which in turn causes cognitive impairment in PH offspring. This study provides a scientific clues for understanding the mechanisms of impaired cognition in PH offspring and provides a theoretical basis for the treatment of cognitive impairment in offspring exposed to PH.
Keywords: Neurology; molecular mechanism of gene regulation; pregnancy.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

