Phytoimmunomodulators: A review of natural modulators for complex immune system
- PMID: 38205318
- PMCID: PMC10777011
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23790
Phytoimmunomodulators: A review of natural modulators for complex immune system
Abstract
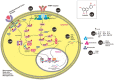
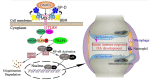
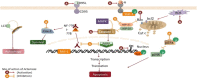
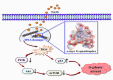
In the past few decades, the medicinal properties of plants and their effects on the human immune system are being studied extensively. Plants are an incredible source of traditional medicines that help cure various diseases, including altered immune mechanisms and are economical and benign compared to allopathic medicines. Reported data in written documents such as Traditional Chinese medicine, Indian Ayurvedic medicine support the supplementation of botanicals for immune defense reactions in the body and can lead to safe and effective immunity responses. Additionally, some botanicals are well-identified as magical herbal remedies because they act upon the pathogen directly and help boost the immunity of the host. Chemical compounds, also known as phytochemicals, obtained from these botanicals looked promising due to their effects on the human immune system by modulating the lymphocytes which subsequently reduce the chances of getting infected. This paper summarises most documented phytochemicals and how they act on the immune system, their properties and possible mechanisms, screening conventions, formulation guidelines, comparison with synthetic immunity-enhancers, marketed immunity-boosting products, and immune-booster role in the ongoing ghastly corona virus wave. However, it focuses mainly on plant metabolites as immunomodulators. In addition, it also sheds light on the current advancements and future possibilities in this field. From this thorough study, it can be stated that the plant-based secondary metabolites contribute significantly to immunity building and could prove to be valuable medicaments for the design and development of novel immunomodulators even for a pandemic like COVID-19.
Keywords: Ayurveda; COVID-19; Immunomodulators; Phytoimmunomodulators; Secondary metabolites; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Herbal Immunomodulators - A Remedial Panacea for Designing and Developing Effective Drugs and Medicines: Current Scenario and Future Prospects.Curr Drug Metab. 2018;19(3):264-301. doi: 10.2174/1389200219666180129125436. Curr Drug Metab. 2018. PMID: 29380694 Review.
-
Mechanism of action of certain medicinal plants for the treatment of asthma.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Dec 5;317:116828. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116828. Epub 2023 Jun 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37369335 Review.
-
Scientific basis for the use of Indian ayurvedic medicinal plants in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders: ashwagandha.Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010 Sep 1;10(3):238-46. doi: 10.2174/1871524911006030238. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20528765 Review.
-
Herbal remedies for urinary stones used in India and China: A review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 May 5;203:55-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.03.038. Epub 2017 Mar 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28344029 Review.
-
Contributions of Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) in the area of Medicinal plants/Traditional medicine.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Feb 2;197:39-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.064. Epub 2016 Jul 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 27452657 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential Role of Plant Polysaccharides in Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 16;16(8):1073. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081073. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medicinal plants: bioactive compounds, biological activities, combating multidrug-resistant microorganisms, and human health benefits - a comprehensive review.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1491777. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1491777. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40375989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Horizons: Recent Advances and Future Prospects in LBDDS for Oral Administration of Antihypertensive Agents.Int J Hypertens. 2024 Feb 19;2024:2430147. doi: 10.1155/2024/2430147. eCollection 2024. Int J Hypertens. 2024. PMID: 38410720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression and intestinal flora in broiler by deep eutectic solvent extracted polysaccharides of Acanthopanax senticosus.Front Vet Sci. 2024 May 27;11:1415716. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1415716. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38863455 Free PMC article.
-
Flow Cytometry-Based Rapid Assay for Antigen Specific Antibody Relative Affinity in SRBC-Immunized Mouse Models.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 12;26(8):3664. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083664. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shukla M.K., Singh S.K., Pandey S., Gupta P.K., Choudhary A., Jindal D.K., Dua K., Kumar D. Potential immunomodulatory activities of plant products. South Afr. J. Bot. 2022;149:937–943. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2022.04.055. - DOI
-
- Dhillon S., Kaur B. Potential benefits of plant-derived immunomodulators. SSRN Electron. J. 2022 doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4095552. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

