Antihypertensive effect and mechanism of the traditional recipe of medicine food homology (Buyang Huanwu Decoction) in China: Meta analysis and network pharmacological exploration
- PMID: 38205319
- PMCID: PMC10776952
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23474
Antihypertensive effect and mechanism of the traditional recipe of medicine food homology (Buyang Huanwu Decoction) in China: Meta analysis and network pharmacological exploration
Abstract
Background: Hypertension has become a part of the lives of many people worldwide. With the development, an increasing number of people have begun to control their hypertension through products of medicine food homology, such as Buyang Huanwu Decoction (BYHWD). However, there has been no objective review of the regulation of hypertension by BYHWD.
Methods: As of 9 October 2023, this review made a detailed search of nine databases to look for random controlled trials (RCTs) focused on the use of BYHWD for treating hypertension. This was followed by network pharmacological analysis, and molecular docking assessment using AutoDockTools to explore the mode of action.
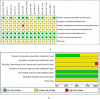
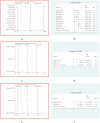
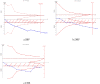
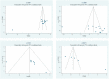
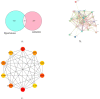
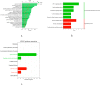
Results: BYHWD was effective in reducing SBP (MD: 0.767; 95 % CI: 0.629, 0.905; p = 0.000), DBP (MD: 0.427; 95 % CI: 0.292, 0.561; p = 0.000), 24h SBP (MD: 0.665; 95 % CI: 0.368, 0.962; p = 0.000), 24h DBP (MD: 0.547; 95 % CI: 0.318, 0.777; p = 0.000), dSBP (MD: 0.625; 95 % CI: 0.395, 0.855; p = 0.000), dDBP (MD: 0.632; 95 % CI: 0.401, 0.862; p = 0.000), nSBP (MD: 0.859; 95 % CI: 0.340, 1.377; p = 0.001), nDBP (MD: 0.704; 95 % CI: 0.297, 1.112; p = 0.001), pv (MD: 1.311; 95 % CI: 0.363, 2.259; p = 0.007) and NIHSS (MD: 1.149; 95 % CI: 0.100, 2.199; p = 0.032), and elevating CER (OR = 2.848; 95 % CI: 1.388, 5.843; p = 0.004). However, BYHWD did not significantly reduce HCY, and there was no significant difference in the incidence of AE. In terms of the mechanism of action, the main active ingredient of BYHWD is quercetin, and the core targets are AKT1, MMP9, and others. Molecular docking also showed that quercetin mainly interacts with the amino acid residue CYS-28 of MMP2. Second, the KEGG analysis showed that BYHWD mainly act on HIF-1, Apelin, and cGMP-PKG signalling pathways, and GO analysis showed that it related to the apical part of the cell, circulatory system processes, and nuclear receptor activity. Conclusion: BYHWD can lowered blood pressure, reduced plasma viscosity, and restored neurological function with good tolerability, and had no significant effect on HCY levels. This study further demonstrated that quercetin is the main active ingredient of BYHWD that acts via the AKT1 and HIF-1 signalling pathways. These results provide new guidance for people's dietary choices by the general public.
Keywords: BYHWD; Hypertension; Medicine food homology; Meta; Molecular docking; Network pharmacology.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Yajun Zhang reports financial support was provided by Inner Mongolia Medical University. Yajun Zhang reports a relationship with Inner Mongolia Medical University that includes: employment. No other influencing factors. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






Similar articles
-
An evidence-based evaluation of Buyang Huanwu decoction for the treatment of the sequelae of stroke: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Phytomedicine. 2022 Sep;104:154312. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154312. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35810520
-
Unraveling the mechanism of tetrandrine combined with Buyang Huanwu Decoction against silicosis using network pharmacology and molecular docking analyses.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Aug 11;102(32):e34716. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034716. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37565873 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active compounds and mechanism of Buyang Huanwu Decoction for ischemic stroke.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Oct;22(4):1050. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10484. Epub 2021 Jul 23. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34434264 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering mechanism of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in regulating macrophage polarization to alleviate atherosclerosis via virtual screening and experimental verification.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Nov 21:119152. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119152. Online ahead of print. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39580134
-
Efficacy evaluation of Buyang Huanwu Decoction in the treatment of ischemic stroke in the recovery period: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 14;13:975816. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.975816. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36313307 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances in the Identification Methods of Food-Medicine Homologous Herbal Materials.Foods. 2025 Feb 12;14(4):608. doi: 10.3390/foods14040608. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40002052 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhou X.L., et al. [Clinical research of Pinggan Jiangya decoction combined with penetrating needling at Baihui (GV20) in a period of day from 7 am to 9 am in the treatment of grade 1 and 2 essential hypertension] Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022;47(2):165–170. - PubMed
-
- Gong X., et al. Hypoglycemic effects of bioactive ingredients from medicine food homology and medicinal health food species used in China. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020;60(14):2303–2326. - PubMed
-
- Tang X., et al. Development and application of one root of medicine and food. Modern Chinese Medicine. 2020;22(9):1428–1433.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

