Huang Gan Formula Alleviates Systemic Inflammation and Uremia in Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Rats May Associate with Modification of Gut Microbiota and Colonic Microenvironment
- PMID: 38205394
- PMCID: PMC10777866
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S421446
Huang Gan Formula Alleviates Systemic Inflammation and Uremia in Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease Rats May Associate with Modification of Gut Microbiota and Colonic Microenvironment
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to investigate the effects of Huang Gan formula (HGF), a Chinese herbal prescription used for chronic kidney disease (CKD), on the regulation of the gut microbiota and colonic microenvironment of CKD.
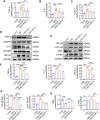
Methods: CKD rats were induced by 150 mg/kg adenine gavage for 4 weeks, then orally treated with or without 3.6 g/kg or 7.2 g/kg of HGF for 8 weeks. The renal function and structure were analyzed by biochemical detection, hematoxylin and eosin, Masson's trichrome, Sirius red and immunochemical staining. Average fecal weight and number in the colon were recorded to assess colonic motility. Further, the changes in the gut microbiota and colonic microenvironment were evaluated by 16S rRNA sequencing, RT-PCR or immunofluorescence. The levels of inflammatory cytokines, uremic toxins, and NF-κB signaling pathway were detected by RT-PCR, ELISA, chloramine-T method or Western blotting. Redundancy analysis biplot and Spearman's rank correlation coefficient were used for correlation analysis.
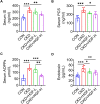
Results: HGF significantly improved renal function and pathological injuries of CKD. HGF could improve gut microbial dysbiosis, protect colonic barrier and promote motility of colonic lumens. Further, HGF inhibited systemic inflammation through a reduction of TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, TGF-β1, and a suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway. The serum levels of the selected uremic toxins were also reduced by HGF treatment. Spearman correlation analysis suggested that high-dose HGF inhibited the overgrowth of bacteria that were positively correlated with inflammatory factors (eg, TNF-α) and uremic toxins (eg, indoxyl sulfate), whereas it promoted the proliferation of bacteria belonging to beneficial microbial groups and was positively correlated with the level of IL-10.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that HGF can improve adenine-induced CKD via suppressing systemic inflammation and uremia, which may associate with the regulations of the gut microbiota and colonic microenvironment.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; colonic microenvironment; gut-kidney axis; systemic inflammation.
© 2024 Zhao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Emodin via colonic irrigation modulates gut microbiota and reduces uremic toxins in rats with chronic kidney disease.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 5;7(14):17468-78. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8160. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27003359 Free PMC article.
-
Uremia-Induced Gut Barrier Defect in 5/6 Nephrectomized Mice Is Worsened by Candida Administration through a Synergy of Uremic Toxin, Lipopolysaccharide, and (1➔3)-β-D-Glucan, but Is Attenuated by Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus L34.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 24;23(5):2511. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052511. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35269654 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid chromatography coupled with high resolution mass spectrometry reveals the inhibitory effects of Huangkuisiwu formula on biosynthesis of protein-binding uremic toxins in rats with chronic kidney disease.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2025 Feb 1;1252:124445. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2024.124445. Epub 2024 Dec 28. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39746293
-
[Pathomechanism and treatment of gut microbiota dysbiosis in chronic kidney disease and interventional effects of Chinese herbal medicine].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Jul;42(13):2425-2432. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170609.014. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28840678 Review. Chinese.
-
The Impact of CKD on Uremic Toxins and Gut Microbiota.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Mar 31;13(4):252. doi: 10.3390/toxins13040252. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33807343 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering the mechanistic basis of Rheum palmatum L. (rhubarb) in the treatment of chronic kidney disease: an integrative approach using network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation.Pharm Biol. 2025 Dec;63(1):582-606. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2025.2543829. Epub 2025 Aug 10. Pharm Biol. 2025. PMID: 40783939 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoferremic Response to Chronic Inflammation Is Controlled via the Hemojuvelin/Hepcidin/Ferroportin Axis and Does Not Involve Hepcidin-Independent Regulation of Fpn mRNA.Am J Hematol. 2025 Aug;100(8):1323-1333. doi: 10.1002/ajh.27710. Epub 2025 May 10. Am J Hematol. 2025. PMID: 40347094 Free PMC article.
-
Shenshuaikang enema restores the intestinal barrier and microbiota-gut-kidney axis balance to alleviate chronic kidney disease via NF-κB pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 21;15:1453668. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1453668. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39906395 Free PMC article.
-
Astragalus Polysaccharide Enhances Voriconazole Metabolism under Inflammatory Conditions through the Gut Microbiota.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024 May 28;12(5):481-495. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00024. Epub 2024 Apr 19. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38779521 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and perspectives in traditional Chinese medicine intervention for uremic pruritus: emphasis on blinding, mechanisms, and safety assessment.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Aug 19. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04742-5. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40828501 No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

