Cell type-specific regulation of m6 A modified RNAs in the aging Drosophila brain
- PMID: 38205931
- PMCID: PMC10928574
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.14076
Cell type-specific regulation of m6 A modified RNAs in the aging Drosophila brain
Abstract
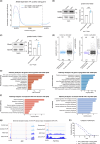
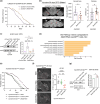
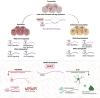
The aging brain is highly vulnerable to cellular stress, and neurons employ numerous mechanisms to combat neurotoxic proteins and promote healthy brain aging. The RNA modification m6 A is highly enriched in the Drosophila brain and is critical for the acute heat stress response of the brain. Here we examine m6 A in the fly brain with the chronic stresses of aging and degenerative disease. m6 A levels dynamically increased with both age and disease in the brain, marking integral neuronal identity and signaling pathway transcripts that decline in level with age and disease. Unexpectedly, there is opposing impact of m6 A transcripts in neurons versus glia, which conferred different outcomes on animal health span upon Mettl3 knockdown to reduce m6 A: whereas Mettl3 function is normally beneficial to neurons, it is deleterious to glia. Moreover, knockdown of Mettl3 in glial tauopathy reduced tau pathology and increased animal survival. These findings provide mechanistic insight into regulation of m6 A modified transcripts with age and disease, highlighting an overall beneficial function of Mettl3 in neurons in response to chronic stresses, versus a deleterious impact in glia.
Keywords: Drosophila; Alzheimer's disease; aging; epitranscriptomics; m6A; neurodegeneration.
© 2024 The Authors. Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mettl3-dependent m6A modification attenuates the brain stress response in Drosophila.Nat Commun. 2022 Sep 14;13(1):5387. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33085-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 36104353 Free PMC article.
-
Tau polarizes an aging transcriptional signature to excitatory neurons and glia.Elife. 2023 May 23;12:e85251. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85251. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37219079 Free PMC article.
-
dTrmt10A impacts Hsp70 chaperone m6A levels and the stress response in the Drosophila brain.Sci Rep. 2023 Dec 28;13(1):22999. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50272-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38155219 Free PMC article.
-
The m6A Dynamics of Profilin in Neurogenesis.Front Genet. 2019 Nov 12;10:987. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00987. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31798620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glial contributions to neuronal health and disease: new insights from Drosophila.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017 Dec;47:162-167. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2017.10.008. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 29096245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulating translation in aging: from global to gene-specific mechanisms.EMBO Rep. 2024 Dec;25(12):5265-5276. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00315-2. Epub 2024 Nov 19. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 39562712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-Methyladenosine Modification on the Function of Female Reproductive Development and Related Diseases.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Dec;12(12):e70089. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70089. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39660878 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bellenguez, C. , Küçükali, F. , Jansen, I. E. , Kleineidam, L. , Moreno‐Grau, S. , Amin, N. , Naj, A. C. , Campos‐Martin, R. , Grenier‐Boley, B. , Andrade, V. , Holmans, P. A. , Boland, A. , Damotte, V. , van der Lee, S. J. , Costa, M. R. , Kuulasmaa, T. , Yang, Q. , de Rojas, I. , Bis, J. C. , … Lambert, J. C. (2022). New insights into the genetic etiology of Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Nature Genetics, 54, 412–436. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berry, R. W. , Quinn, B. , Johnson, N. , Cochran, E. J. , Ghoshal, N. , & Binder, L. I. (2001). Pathological glial tau accumulations in neurodegenerative disease: Review and case report. Neurochemistry International, 39, 469–479. - PubMed
-
- Bolukbasi, E. , Woodling, N. S. , Ivanov, D. K. , Adcott, J. , Foley, A. , Rajasingam, A. , Gittings, L. M. , Aleyakpo, B. , Niccoli, T. , Thornton, J. M. , & Partridge, L. (2021). Cell type‐specific modulation of healthspan by Forkhead family transcription factors in the nervous system. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 118, e2011491118. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

