Clinical significance and prospective mechanism of increased CDKN2A expression in small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 38206516
- PMCID: PMC11108933
- DOI: 10.1007/s12094-023-03376-2
Clinical significance and prospective mechanism of increased CDKN2A expression in small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Although it has been shown that cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A (CDKN2A) plays a significant role in a number of malignancies, its clinicopathological value and function in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is unclear and warrants additional research.
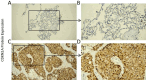
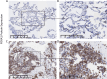
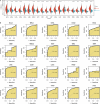
Methods: The clinical significance of CDKN2A expression in SCLC was examined by multiple methods, including comprehensive integration of mRNA level by high throughput data, Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for prognostic value, and validation of its protein expression using in-house immunohistochemistry.
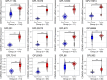
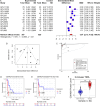
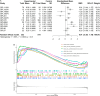
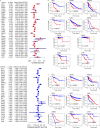
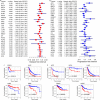
Results: The expression of CDKN2A mRNA in 357 cases of SCLC was evidently higher than that in the control group (n = 525) combing the data from 20 research centers worldwide. The standardized mean difference (SMD) was 3.07, and the area under the curve (AUC) of summary receiver operating characteristic curve (sROC) was 0.97 for the overexpression of CDKN2A. ACC, COAD, KICH, KIRC, PCPG, PRAD, UCEC, UVM patients with higher CDKN2A expression had considerably worse overall survival rates than those with lower CDKN2A expression with the hazard ratio (HR) > 1.
Conclusion: CDKN2A upregulation extensively enhances the carcinogenesis and progression of SCLC.
Keywords: Clinical significance; Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2A; Immunohistochemistry; Kaplan–Meier survival analysis; Small cell lung cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An immunohistochemical study of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC): a possible prognostic biomarker.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Feb 9;14(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0787-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26860827 Free PMC article.
-
High expression of oncoprotein DEK predicts poor prognosis of small cell lung cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Jul 15;7(8):5016-23. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25197373 Free PMC article.
-
ITGB4 Serves as an Identification and Prognosis Marker Associated with Immune Infiltration in Small Cell Lung Carcinoma.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Oct;66(10):2956-2971. doi: 10.1007/s12033-023-00912-x. Epub 2023 Oct 17. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37847361
-
Clinical significance of NQO1 polymorphism and expression of p53, SOD2, PARP1 in limited-stage small cell lung cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Sep 15;7(10):6743-51. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25400754 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of thyroid transcription factor-1 expression in small cell lung cancer: A systemic review and meta-analysis.Pathol Res Pract. 2019 Dec;215(12):152706. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152706. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Pathol Res Pract. 2019. PMID: 31704153
Cited by
-
Epigenetic Modifications as Novel Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapeutic Targeting in Thyroid, Pancreas, and Lung Neuroendocrine Tumors.J Clin Med. 2025 Apr 11;14(8):2622. doi: 10.3390/jcm14082622. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40283452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modifications in early stage lung cancer: pathogenesis, biomarkers, and early diagnosis.MedComm (2020). 2025 Feb 21;6(3):e70080. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70080. eCollection 2025 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 39991629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the oncogenic role of Rac family small GTPase 3 in hepatocellular carcinoma through multiomics integration.World J Hepatol. 2025 Jul 27;17(7):106151. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106151. World J Hepatol. 2025. PMID: 40747231 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S2020031/Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Medical Health Appropriate Technology Development and Application Promotion Project
- GXMUZDJC2223/Guangxi Medical University Key Textbook Construction Project
- Z-A20220459/The Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Health Committee Self-Financed Scientific Research Project
- Z20210132/The Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Health Committee Self-Financed Scientific Research Project
- S202310598176/Guangxi Medical University Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program Project
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

