Comparative Growth Outcomes in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: Evaluating Different Feeding Strategies
- PMID: 38206546
- PMCID: PMC11913907
- DOI: 10.1007/s12098-023-04989-9
Comparative Growth Outcomes in Very Low Birth Weight Infants: Evaluating Different Feeding Strategies
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the growth pattern of preterm, very low birth weight (VLBW) appropriate for gestational age (AGA) infants on three different feeding regimens.
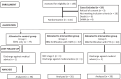
Methods: This prospective open label three-arm parallel randomized controlled trial was conducted at neonatal intensive care unit, Kasturba Hospital, Manipal. One hundred twenty VLBW (weight between 1000-1500 g and gestational age 28-32 wk) preterm AGA infants admitted from April 2021 through September 2022 were included. Three feeding regimens were compared: Expressed breast milk (EBM); EBM supplemented with Human milk fortifier (HMF); EBM supplemented with Preterm formula feed (PTF). Primary outcome measure was assessing the growth parameters such as weight, length, head circumference on three different feeding regimens at birth 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 wk/discharge. Secondary outcomes included incidence of co-morbidities and cost-effectiveness.
Results: Of 112 infants analyzed, Group 2 supplemented with HMF showed superior growth outcomes by 6th wk/discharge of intervention, with mean weight of 2053±251 g, mean length of 44.6±1.9 cm, and mean head circumference of 32.9±1.4 cm. However, infants in Group 3, supplemented with PTF, registered mean weight of 1968±203 g, mean length of 43.6±2.0 cm, and mean head circumference of 32.0±1.6 cm. Infants exclusively on EBM presented with mean weight of 1873±256 g, mean length of 43.0±2.0 cm and mean head circumference of 31.4±1.6 cm.
Conclusions: Addition of 1 g of HMF to 25 ml of EBM in neonates weighing 1000-1500 g showed better weight gain and head circumference at 6 wk/discharge, which was statistically significant. However, no significant differences in these parameters were observed at postnatal or 2, 3, 4, and 5 wk.
Keywords: Human milk; Human milk fortification; Neonates; Preterm.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures
References
-
- Gupta V, Rebekah G, Sudhakar Y, Santhanam S, Kumar M, Thomas N. A randomized controlled trial comparing the effect of fortification of human milk with an infant formula powder versus unfortified human milk on the growth of preterm very low birth weight infants. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33:2507–15. - PubMed
-
- Bauer J, Gerss J. Longitudinal analysis of macronutrients and minerals in human milk produced by mothers of preterm infants. Clin Nutr. 2011;30:215–20. - PubMed
-
- O’Connor DL, Kiss A, Tomlinson C, et al. Nutrient enrichment of human milk with human and bovine milk-based fortifiers for infants born weighing <1250 g: a randomized clinical trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2018;108:108–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous