A Biomechanics-Aware Robot-Assisted Steerable Drilling Framework for Minimally Invasive Spinal Fixation Procedures
- PMID: 38206784
- PMCID: PMC11168586
- DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2024.3352607
A Biomechanics-Aware Robot-Assisted Steerable Drilling Framework for Minimally Invasive Spinal Fixation Procedures
Abstract
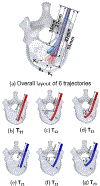
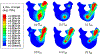
In this paper, we propose a novel biomechanics-aware robot-assisted steerable drilling framework with the goal of addressing common complications of spinal fixation procedures occurring due to the rigidity of drilling instruments and implants. This framework is composed of two main unique modules to design a robotic system including (i) a Patient-Specific Biomechanics-aware Trajectory Selection Module used to analyze the stress and strain distribution along an implanted pedicle screw in a generic drilling trajectory (linear and/or curved) and obtain an optimal trajectory; and (ii) a complementary semi-autonomous robotic drilling module that consists of a novel Concentric Tube Steerable Drilling Robot (CT-SDR) integrated with a seven degree-of-freedom robotic manipulator. This semi-autonomous robot-assisted steerable drilling system follows a multi-step drilling procedure to accurately and reliably execute the optimal hybrid drilling trajectory (HDT) obtained by the Trajectory Selection Module. Performance of the proposed framework has been thoroughly analyzed on simulated bone materials by drilling various trajectories obtained from the finite element-based Selection Module using Quantitative Computed Tomography (QCT) scans of a real patient's vertebra.
Figures


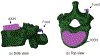

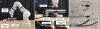

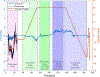
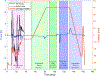
Similar articles
-
A Concentric Tube Steerable Drilling Robot for Minimally Invasive Spinal Fixation of Osteoporotic Vertebrae.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023 Nov;70(11):3017-3027. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2023.3272306. Epub 2023 Oct 19. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2023. PMID: 37130252 Free PMC article.
-
Robot-assisted Percutaneous Transfacet Screw Fixation Supplementing Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion Procedure: Accuracy and Safety Evaluation of This Novel Minimally Invasive Technique.Orthop Surg. 2019 Feb;11(1):25-33. doi: 10.1111/os.12428. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Orthop Surg. 2019. PMID: 30776856 Free PMC article.
-
A Synergistic Patient-Specific Approach for Enhanced Spinal Fixation Using a Novel Flexible Pedicle Screw and a Complementary Steerable Drilling Robotic System.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2025 Jun 9;PP. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2025.3578540. Online ahead of print. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2025. PMID: 40489262
-
Robotic-assisted cortical bone trajectory (CBT) screws using the Mazor X Stealth Edition (MXSE) system: workflow and technical tips for safe and efficient use.J Robot Surg. 2021 Feb;15(1):13-23. doi: 10.1007/s11701-020-01147-7. Epub 2020 Sep 28. J Robot Surg. 2021. PMID: 32989623 Review.
-
Cortical Bone Trajectory for Lumbar Pedicle Screw Placement: A Review of Published Reports.Orthop Surg. 2015 Aug;7(3):213-21. doi: 10.1111/os.12185. Orthop Surg. 2015. PMID: 26311095 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gaines RW Jr, “The use of pedicle-screw internal fixation for the operative treatment of spinal disorders,” JBJS, vol. 82, no. 10, p. 1458, 2000. - PubMed
-
- Rometsch E, Spruit M, Zigler JE, Menon VK, Ouellet JA, Mazel C, Härtl R, Espinoza K, and Kandziora F, “Screw-related complications after instrumentation of the osteoporotic spine: a systematic literature review with meta-analysis,” Global spine journal, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 69–88, 2020. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weiser L, Huber G, Sellenschloh K, Viezens L, Püschel K, Morlock MM, and Lehmann W, “Insufficient stability of pedicle screws in osteoporotic vertebrae: biomechanical correlation of bone mineral density and pedicle screw fixation strength,” European Spine Journal, vol. 26, no. 11, pp. 2891–2897, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Alambeigi F, Bakhtiarinejad M, Sefati S, Hegeman R, Iordachita I, Khanuja H, and Armand M, “On the use of a continuum manipulator and a bendable medical screw for minimally invasive interventions in orthopedic surgery,” IEEE transactions on medical robotics and bionics, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 14–21, 2019. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alambeigi F, Wang Y, Sefati S, Gao C, Murphy R, Iordachita I, Taylor R, and Khanuja H, “A curved-drilling approach in core decompression of the femoral head osteonecrosis using a continuum manipulator,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. PP, pp. 1–1, 02 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

