Assessment of antimalarial activity of crude extract of Chan-Ta-Lee-La and Pra-Sa-Chan-Dang formulations and their plant ingredients for new drug candidates of malaria treatment: In vitro and in vivo experiments
- PMID: 38206944
- PMCID: PMC10783769
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296756
Assessment of antimalarial activity of crude extract of Chan-Ta-Lee-La and Pra-Sa-Chan-Dang formulations and their plant ingredients for new drug candidates of malaria treatment: In vitro and in vivo experiments
Abstract
The emergence and spread of antimalarial drug resistance have become a significant problem worldwide. The search for natural products to develop novel antimalarial drugs is challenging. Therefore, this study aimed to assess the antimalarial and toxicological effects of Chan-Ta-Lee-La (CTLL) and Pra-Sa-Chan-Dang (PSCD) formulations and their plant ingredients. The crude extracts of CTLL and PSCD formulations and their plant ingredients were evaluated for in vitro antimalarial activity using Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase enzyme and toxicity to Vero and HepG2 cells using the tetrazolium salt method. An extract from the CTLL and PSCD formulations exhibiting the highest selectivity index value was selected for further investigation using Peter's 4-day suppressive test, curative test, prophylactic test, and acute oral toxicity in mice. The phytochemical constituents were characterized using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Results showed that ethanolic extracts of CTLL and PSCD formulations possessed high antimalarial activity (half maximal inhibitory concentration = 4.88, and 4.19 g/mL, respectively) with low cytotoxicity. Ethanolic extracts of the CTLL and PSCD formulations demonstrated a significant dose-dependent decrease in parasitemia in mice. The ethanolic CTLL extract showed the greatest suppressive effect after 4 days of suppressive (89.80%) and curative (35.94%) testing at a dose of 600 mg/kg. Moreover, ethanolic PSCD extract showed the highest suppressive effect in the prophylactic test (65.82%) at a dose of 600 mg/kg. There was no acute toxicity in mice treated with ethanolic CTLL and PSCD extracts at 2,000 mg/kg bodyweight. GC-MS analysis revealed that the most abundant compounds in the ethanolic CTLL extract were linderol, isoborneol, eudesmol, linoleic acid, and oleic acid, whereas ethyl 4-methoxycinnamate was the most commonly found compound in the ethanolic PSCD extract, followed by 3-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one, flamenol, oleic acid amide, linoleic acid, and oleic acid. In conclusions, ethanolic CTLL and PSCD extracts exhibited high antimalarial efficacy in vitro. The ethanolic CTLL extract at a dose of 600 mg/kg exhibited the highest antimalarial activity in the 4-day suppressive and curative tests, whereas the ethanolic PSCD extract at a dose of 600 mg/kg showed the highest antimalarial activity in the prophylactic test.
Copyright: © 2024 Chaniad et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

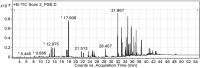
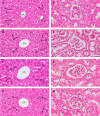
Similar articles
-
In vivo assessment of the antimalarial activity and acute oral toxicity of an ethanolic seed extract of Spondias pinnata (L.f.) Kurz.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Mar 16;22(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03546-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35296314 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical evaluation of antimalarial activity of CPF-1 formulation as an alternative choice for the treatment of malaria.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 May 4;23(1):144. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03973-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37143036 Free PMC article.
-
Antimalarial efficacy of Pongamia pinnata (L) Pierre against Plasmodium falciparum (3D7 strain) and Plasmodium berghei (ANKA).BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Sep 11;17(1):458. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1958-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. Retraction in: BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 May 10;21(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03312-3. PMID: 28893216 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Antimalarial efficacy and toxicological assessment of medicinal plant ingredients of Prabchompoothaweep remedy as a candidate for antimalarial drug development.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Jan 18;23(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-03835-x. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 36653791 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the antimalarial activity and toxicity of Mahanil-Tang-Thong formulation and its plant ingredients.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Feb 27;22(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03531-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35219319 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antimalarial efficacy test of the aqueous crude leaf extract of Coriandrum sativum Linn.: an in vivo multiple model experimental study in mice infected with Plasmodium berghei.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Jul 12;24(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04577-0. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 38997693 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential antimalarial properties, safety profile, and phytochemical composition of Mesua ferrea Linn.PLoS One. 2024 Dec 2;19(12):e0312047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312047. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39621736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lohakul J, Chaiprasongsuk A, Jeayeng S, Saelim M, Muanjumpon P, Thanachaiphiwat S, et al.. The protective effect of polyherbal formulation, harak formula, on UVA-induced photoaging of human dermal fibroblasts and mouse skin via promoting Nrf2-regulated antioxidant defense. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:649820. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.649820 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smita GB. Medicinal plants and its pharmacological values. In: Natural Medicinal Plants. edn. Edited by Hany AE-S. Rijeka: IntechOpen; 2021: Ch. 12. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.99848 - DOI
-
- WHO. Antimicrobial resistance [cited 2023 4]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

