Local and Sustained Baricitinib Delivery to the Skin through Injectable Hydrogels Containing Reversible Thioimidate Adducts
- PMID: 38207170
- PMCID: PMC11076163
- DOI: 10.1002/adhm.202303256
Local and Sustained Baricitinib Delivery to the Skin through Injectable Hydrogels Containing Reversible Thioimidate Adducts
Abstract
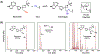
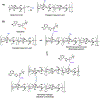
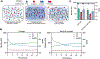
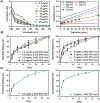
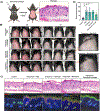
Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are approved for many dermatologic disorders, but their use is limited by systemic toxicities including serious cardiovascular events and malignancy. To overcome these limitations, injectable hydrogels are engineered for the local and sustained delivery of baricitinib, a representative JAK inhibitor. Hydrogels are formed via disulfide crosslinking of thiolated hyaluronic acid macromers. Dynamic thioimidate bonds are introduced between the thiolated hyaluronic acid and nitrile-containing baricitinib for drug tethering, which is confirmed with 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Release of baricitinib is tunable over six weeks in vitro and active in inhibiting JAK signaling in a cell line containing a luciferase reporter reflecting interferon signaling. For in vivo activity, baricitinib hydrogels or controls are injected intradermally into an imiquimod-induced mouse model of psoriasis. Imiquimod increases epidermal thickness in mice, which is unaffected when treated with baricitinib or hydrogel alone. Treatment with baricitinib hydrogels suppresses the increased epidermal thickness in mice treated with imiquimod, suggesting that the sustained and local release of baricitinib is important for a therapeutic outcome. This study is the first to utilize a thioimidate chemistry to deliver JAK inhibitors to the skin through injectable hydrogels, which has translational potential for treating inflammatory disorders.
Keywords: JAK‐STAT; dermatology; hydrogel; psoriasis; thioimidate.
© 2024 Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Figures
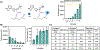


Similar articles
-
Topical delivery of baricitinib-impregnated nanoemulgel: a promising platform for inhibition of JAK -STAT pathway for the effective management of atopic dermatitis.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jun;15(6):2200-2219. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01732-5. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39467941
-
Effect of baricitinib in regulating programmed death 1 and ligand programmed cell death ligand 1 through JAK/STAT pathway in psoriasis.Indian J Pharmacol. 2022 May-Jun;54(3):183-193. doi: 10.4103/ijp.ijp_1089_20. Indian J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35848689 Free PMC article.
-
Baricitinib counteracts metaflammation, thus protecting against diet-induced metabolic abnormalities in mice.Mol Metab. 2020 Sep;39:101009. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101009. Epub 2020 May 13. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32413585 Free PMC article.
-
Baricitinib: therapeutic potential for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020 Oct;29(10):1089-1098. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2020.1800639. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32703039 Review.
-
Baricitinib: From Rheumatoid Arthritis to COVID-19.J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;61(10):1274-1285. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1874. Epub 2021 Jun 12. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33870531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Topical Therapy in Psoriasis: Clinical Benefits, Advances in Novel Drug Delivery Strategies, and Gene Therapy Regimen.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Feb 20;17(3):283. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17030283. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40142947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kozera E, Flora A & Frew JW Real-world safety and clinical response of Janus kinase inhibitor upadacitinib in the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: A retrospective cohort study. J Am Acad Dermatol 87, 1440–1442 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

